This ALMA image reveals much finer structure in the U Antliae shell than has previously been possible. Around 2700 years ago, U Antliae went through a short period of rapid mass loss. During this period of only a few hundred years, the material making up the shell seen in the new ALMA data was ejected at high speed. Examination of this shell in further detail also shows some evidence of thin, wispy clouds known as filamentary substructures.


A Cosmic Eyelash Reveals New Information on Star Formation
This ALMA image shows the Cosmic Eyelash, a remote starburst galaxy that appears double and brightened by gravitational lensing. ALMA has been used to detect turbulent reservoirs of cold gas surrounding this and other distant starburst galaxies. By detecting CH+ for the first time in the distant Universe, this research opens up a new window of exploration into a critical epoch of star formation.
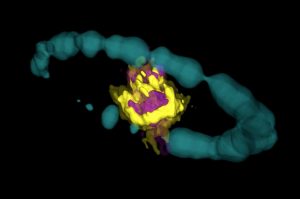
Heart of an Exploded Star Observed in 3-D
Remnant of Supernova 1987A as seen by ALMA. Purple area indicates emission from SiO molecules. Yellow area is emission from CO molecules. The blue ring is Hubble data that has been artificially expanded into 3-D.
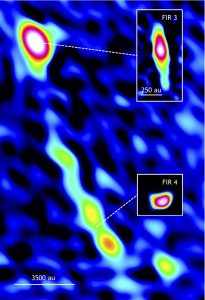
Star’s Birth May Have Triggered Another Star Birth
Protostar FIR 3 (HOPS 370) with outflow that may have triggered the formation of younger protostar FIR 4 (HOPS 108), in the Orion star-forming region. Pullouts are individual VLA images of each protostar. (au = astronomical unit, the distance from the Earth to the Sun, about 93 million miles.)
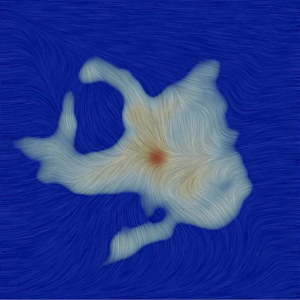
The Magnetic Field of Ser-emb 8
Texture represents the magnetic field orientation in the region surrounding the Ser-emb 8 protostar, as measured by ALMA. The gray region is the millimeter wavelength dust emission.
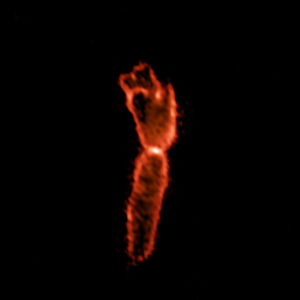
The Ultra-Cold Outflow of the Boomerang Nebula
The Boomerang Nebula, a pre-planetary nebula produced by a dying star. ALMA observations show the hourglass-shaped outflow, which is embedded inside a roughly round ultra-cold outflow. The hourglass outflow stretches more than three trillion kilometers from end to end (about 21,000 times the distance from the Sun to the Earth), and is the result of a jet that is being fired by the central star, sweeping up the inner regions of the ultra-cold outflow like a snow-plow. The ultra-cold outflow is about 10 times bigger.





