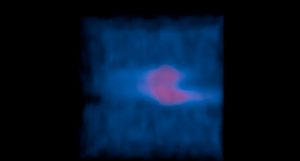
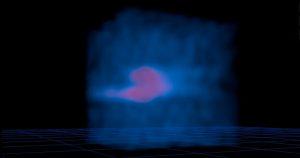
Composite image of the Boomerang Nebula, a pre-planetary nebula produced by a dying star. ALMA observations (orange) showing the hourglass-shaped outflow, which is embedded inside a roughly round ultra-cold outflow. The hourglass outflow stretches more than three trillion kilometers from end to end (about 21,000 times the distance from the Sun to the Earth), and is the result of a jet that is being fired by the central star, sweeping up the inner regions of the ultra-cold outflow like a snow-plow. The ultra-cold outflow is about 10 times bigger. The ALMA data are shown on top of an image from the Hubble Space Telescope (blue).

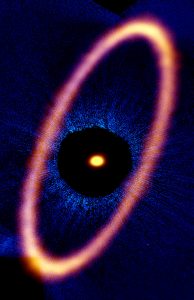
ALMA Eyes Icy Ring around Young Planetary System
Composite image of the Fomalhaut star system. The ALMA data, shown in orange, reveal the distant and eccentric debris disk in never-before-seen detail. The central dot is the unresolved emission from the star, which is about twice the mass of our sun. Optical data from the Hubble Space Telescope is in blue; the dark region is a coronagraphic mask, which filtered out the otherwise overwhelming light of the central star.
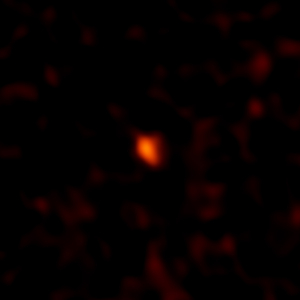
ALMA’s Millimeter Image of DeeDee
ALMA image of the faint millimeter-wavelength “glow” from the planetary body 2014 UZ224, more informally known as DeeDee. At three times the distance of Pluto from the Sun, DeeDee is the second most distant known TNO with a confirmed orbit in our solar system.