This animation shows the motions of the gas streamers emanating from the OMC-1 star-forming region in Orion as seen with ALMA. The colors in the ALMA data represent the relative Doppler shifting of the millimeter-wavelength light emitted by carbon monoxide gas. Initially, the blue color in the ALMA data represents gas approaching at the highest speeds; the red color is from gas moving toward us more slowly. The video then briefly shows gas at rest with respect to the Orion clouds, followed by streamers receding on the other side with even greater speed. Finally, the animation blends into a near-infrared view from the Gemini South telescope showing shock waves produced by the explosion. The explosion occurred about 500 years ago when several young stars were ejected from the region.


The Birth of Supernova 1987A: animation depicting the buildup and aftermath of supernova 1987A
This scientific visualization illustrates the evolution of Supernova 1987A from the initial swelling of the host star and supernova explosion to the expanding shock wave and the formation of molecules detected by ALMA in the remnant.

Animation of a Black Hole
Artist’s conception of region near the supermassive black hole inside the radio galaxy known as 3C 120, where twisted magnetic fields propel and shape jets of particles.
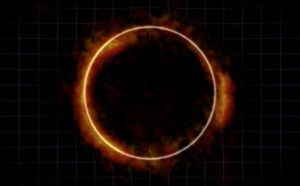
Animation of a Gravitational Lens Creating an Einstein Ring
Animation demonstrating how the gravity from a massive foreground galaxy can bend the light of a more distant galaxy. If the two galaxies line up just right, the result is a highly distorted image of the distant galaxy known as an Einstein ring. The radio image portion of the video is of galaxy SDP.81, which was imaged by ALMA as part of the telescope’s Long Baseline Campaign.

Round and Round the Microquasar Goes
Path of the microquasar (red) known as Scorpius X-1 compared with the path of the Sun (yellow) through the Milky Way Galaxy for the past 230 million years. A microquasar is a pair of interacting stars where one of them is usually a dead star, such as a neutron star or a black hole. Material from the normal star is streaming around and on to the remnant, creating a disk of material. Magnetic fields wreak havoc on the material, whipping it up and out of the disk as enormous jets.





