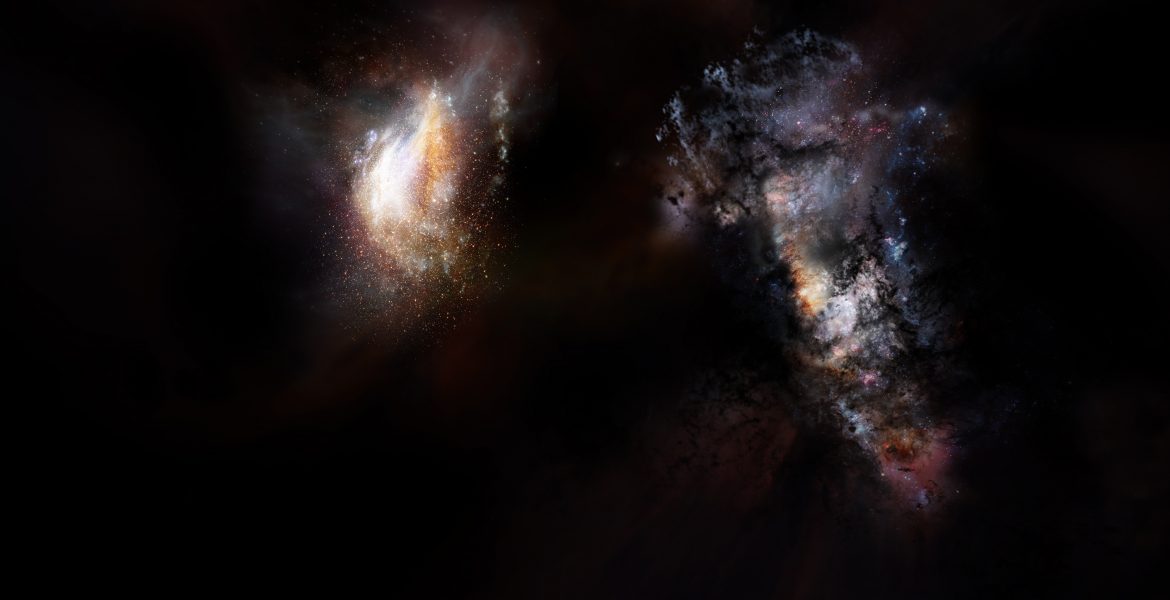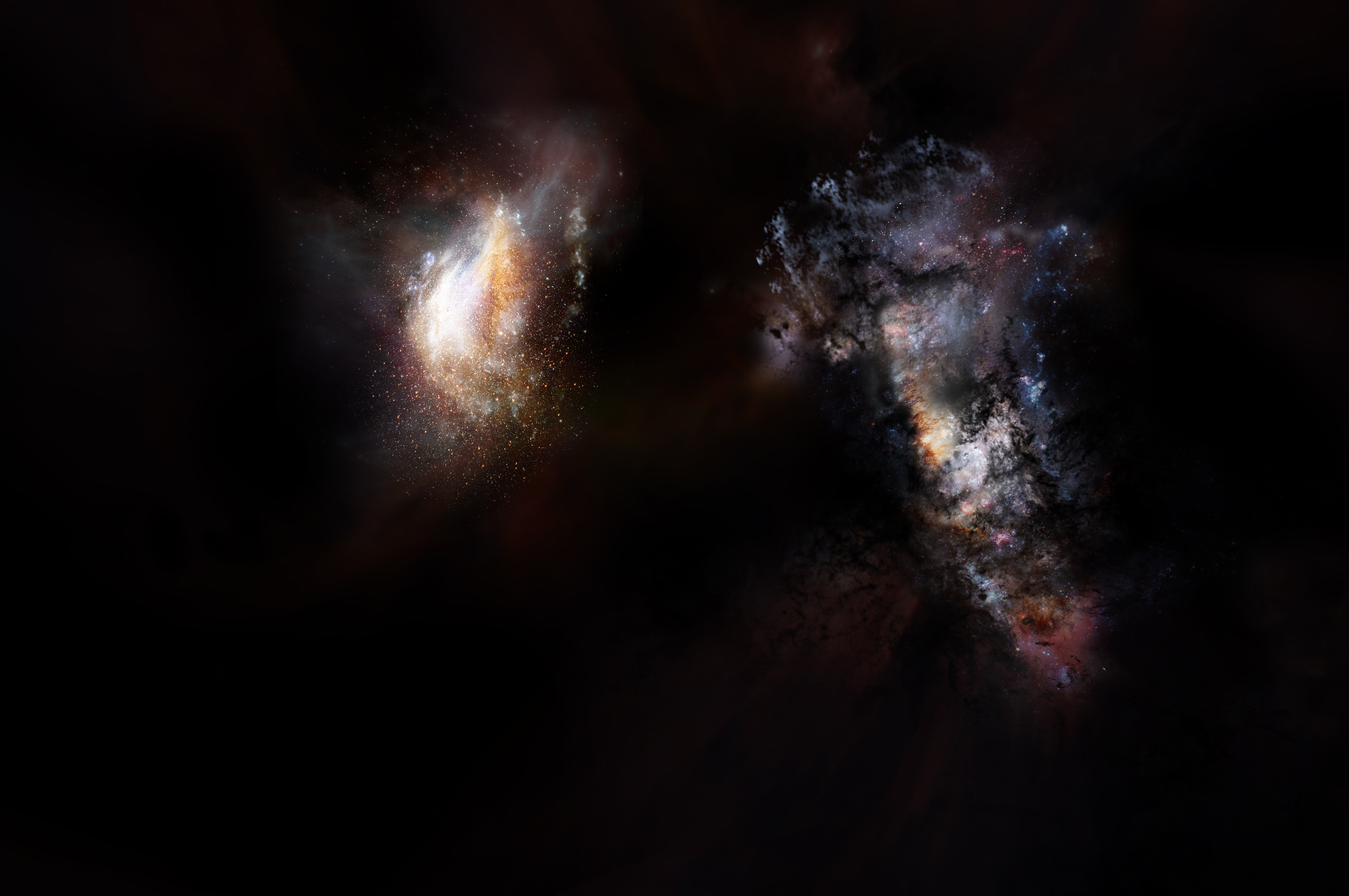Astronomers expect that the first galaxies, those that formed just a few hundred million years after the Big BangBig BangThe well-supported theory that some 13.8 billion years ago, the entire universe was staggeringly small, hot, and dense. In a fraction of an instant, the universe expanded and continues to expand to this day. , would share many similarities with some of the dwarf galaxiesDwarf GalaxyA galaxy that is significantly smaller in size compared to a normal galaxy. Dwarf galaxies are low in luminosity, and often irregular or elliptical in shape. we see in the nearby universe today. These early agglomerations of a few billion stars would then become the building blocks of the larger galaxies that came to dominate the universe after the first few billion years.
Ongoing observations with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter ArrayAtacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA)Funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation and its international partners (NRAO/ESO/NAOJ), ALMA is among the most complex and powerful astronomical observatories on Earth or in space. The telescope is an array of 66 high-precision dish antennas in northern Chile. (ALMA), however, have discovered surprising examples of massive, star-filled galaxies seen when the cosmos was less than a billion years old. This suggests that smaller galactic building blocks were able to assemble into large galaxies quite quickly.
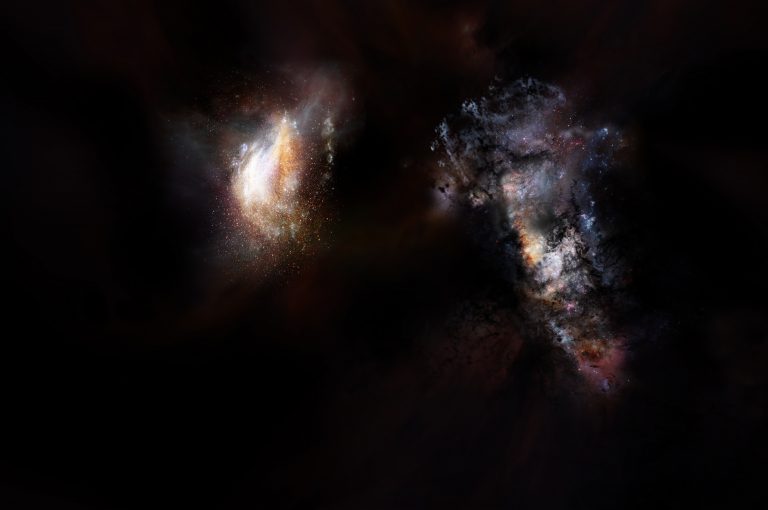
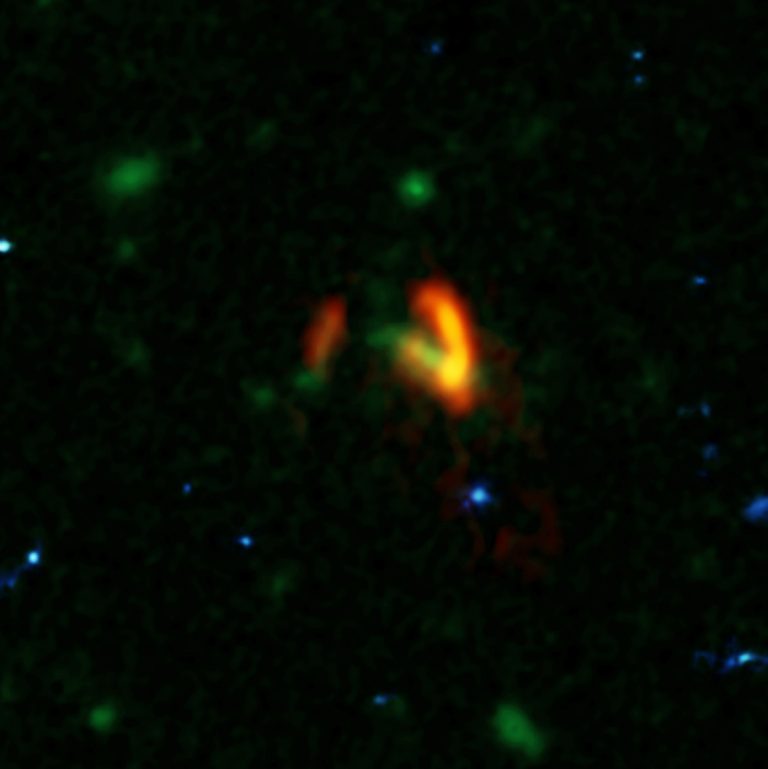
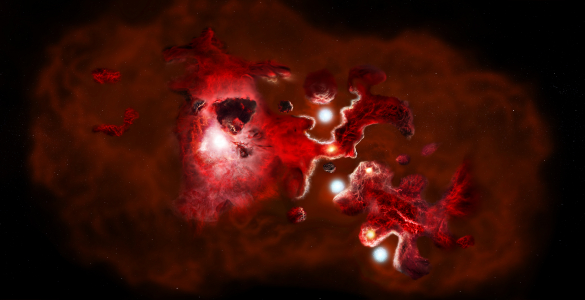
The latest ALMA observations push back this epoch of massive-galaxy formation even further by identifying two giant galaxies seen when the universe was only 780 million years old, or about 5 percent its current age. ALMA also revealed that these uncommonly large galaxies are nestled inside an even-more-massive cosmic structure, a halo of dark matterDark matterA type of matter that does not interact with or emit visible light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation, as far as we know. Its existence is inferred by its obvious gravitational effects. several trillion times more massive than the sun.
The two galaxies are in such close proximity — less than the distance from the Earth to the center of our galaxy — that they will shortly merge to form the largest galaxy ever observed at that period in cosmic history. This discovery provides new details about the emergence of large galaxies and the role that dark matter plays in assembling the most massive structures in the universe.
The researchers report their findings in the journal Nature.
“With these exquisite ALMA observations, astronomers are seeing the most massive galaxy known in the first billion years of the universe in the process of assembling itself,” said Dan Marrone, associate professor of astronomy at the University of Arizona in Tucson and lead author on the paper.
Astronomers are seeing these galaxies during a period of cosmic history known as the Epoch of Reionization, when most of intergalactic space was suffused with an obscuring fog of cold hydrogen gas. As more stars and galaxies formed, their energy eventually ionized the hydrogen between the galaxies, revealing the universe as we see it today.
“We usually view that as the time of little galaxies working hard to chew away at the neutral intergalactic medium,” said Marrone. “Mounting observational evidence with ALMA, however, has helped to reshape that story and continues to push back the time at which truly massive galaxies first emerged in the universe.”
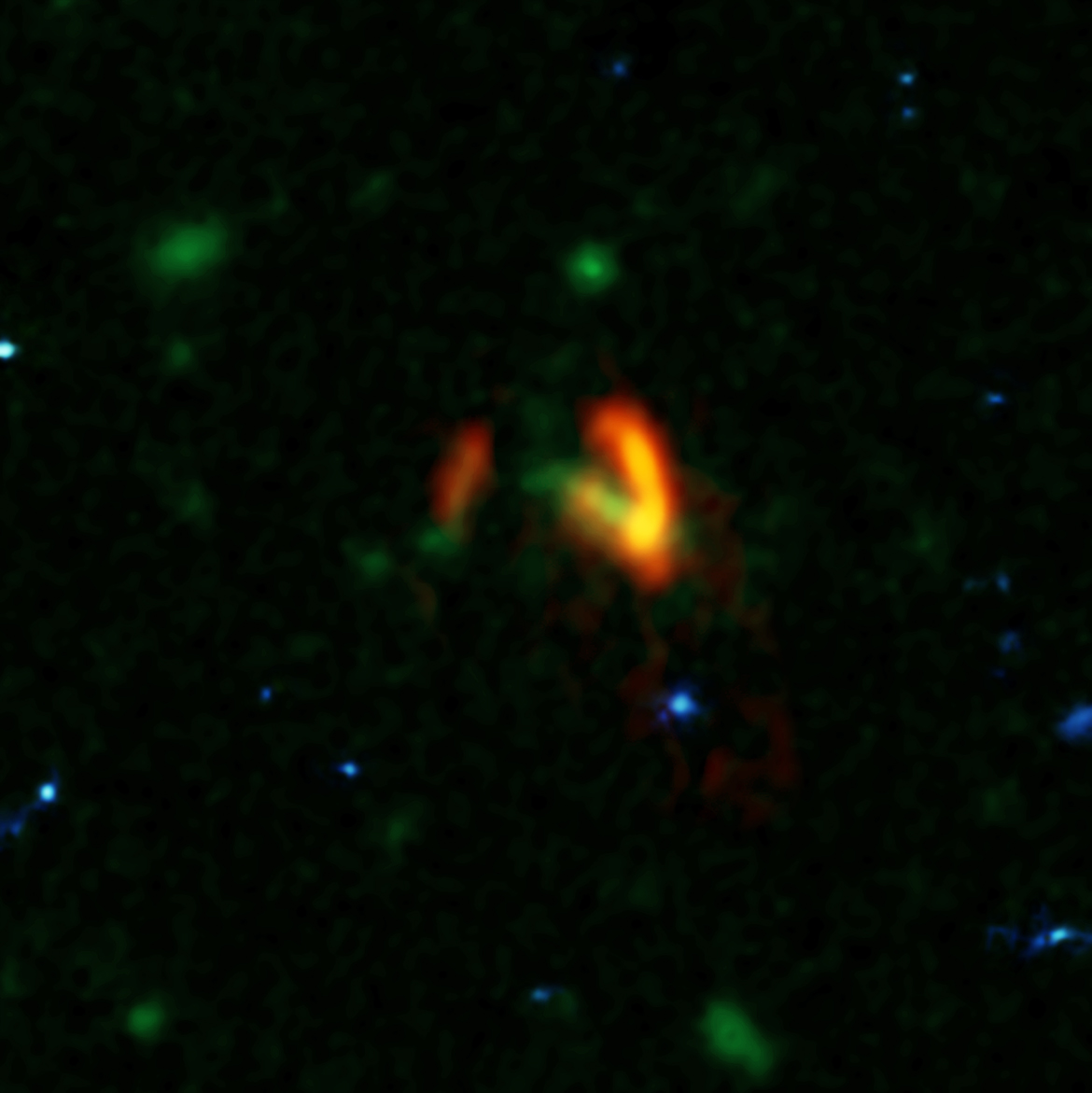
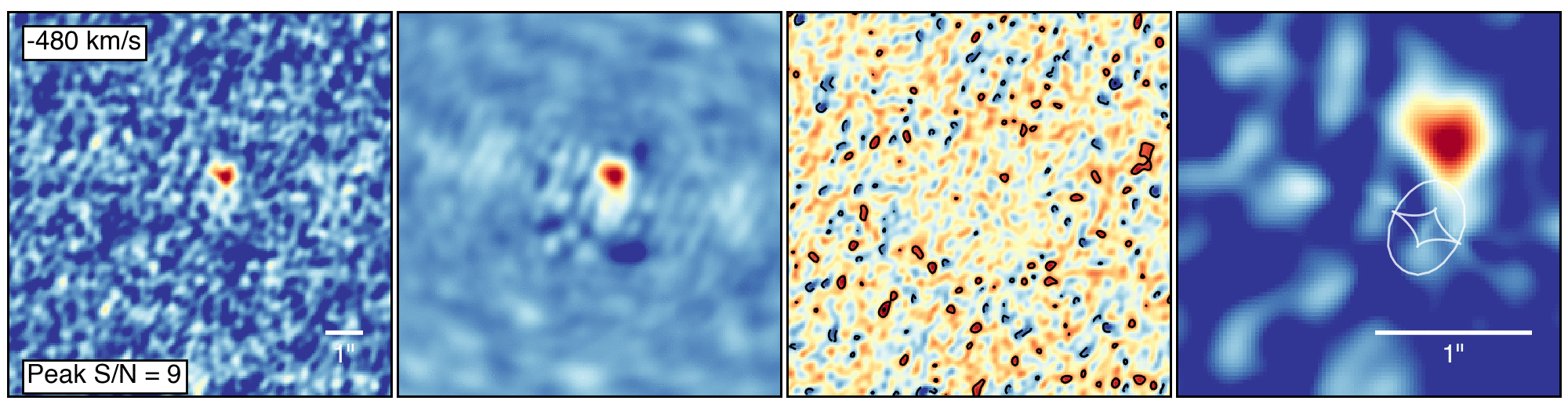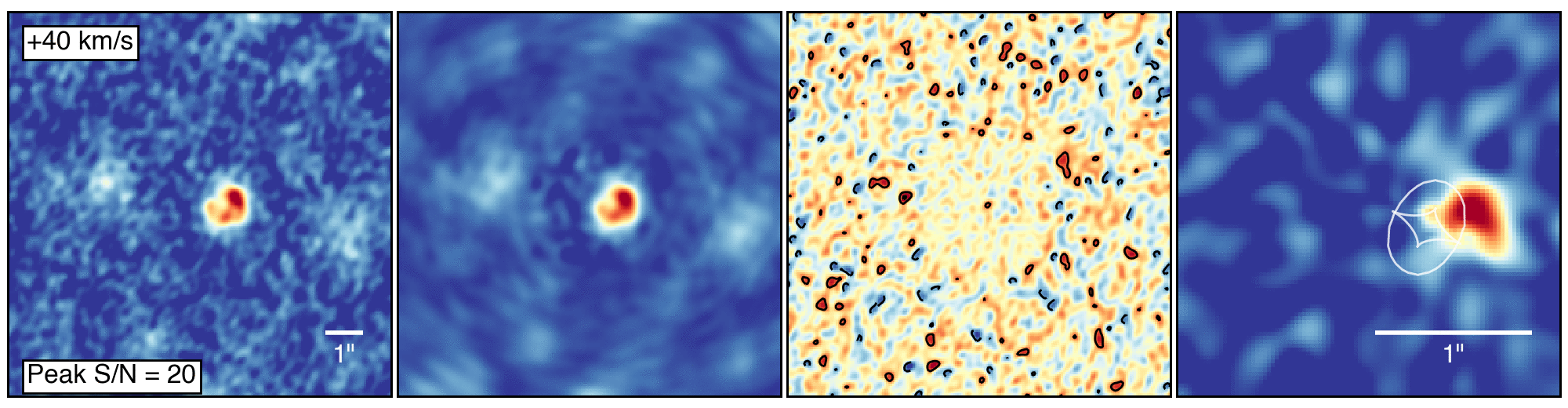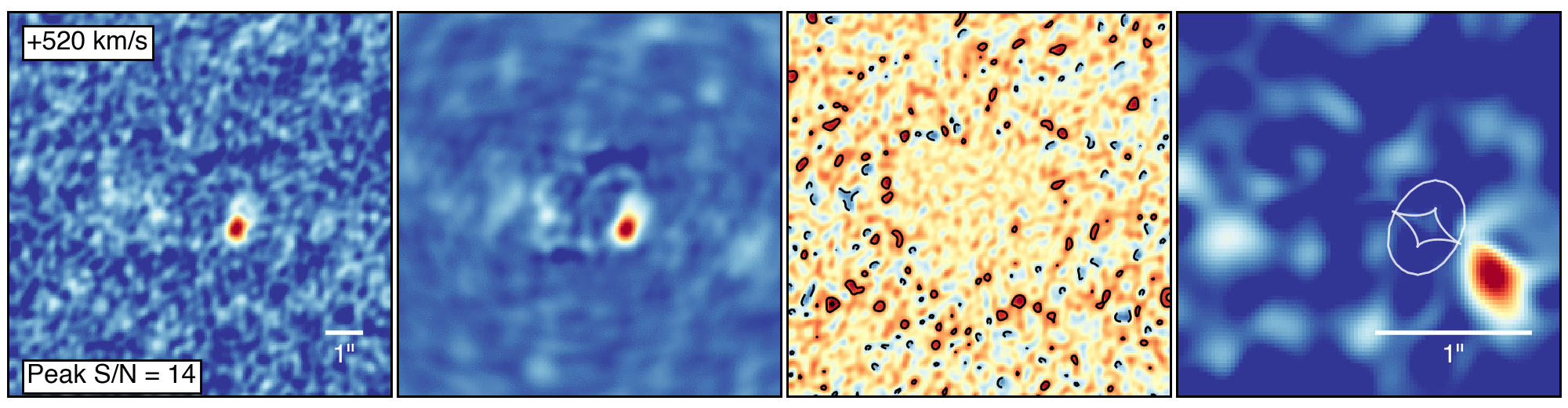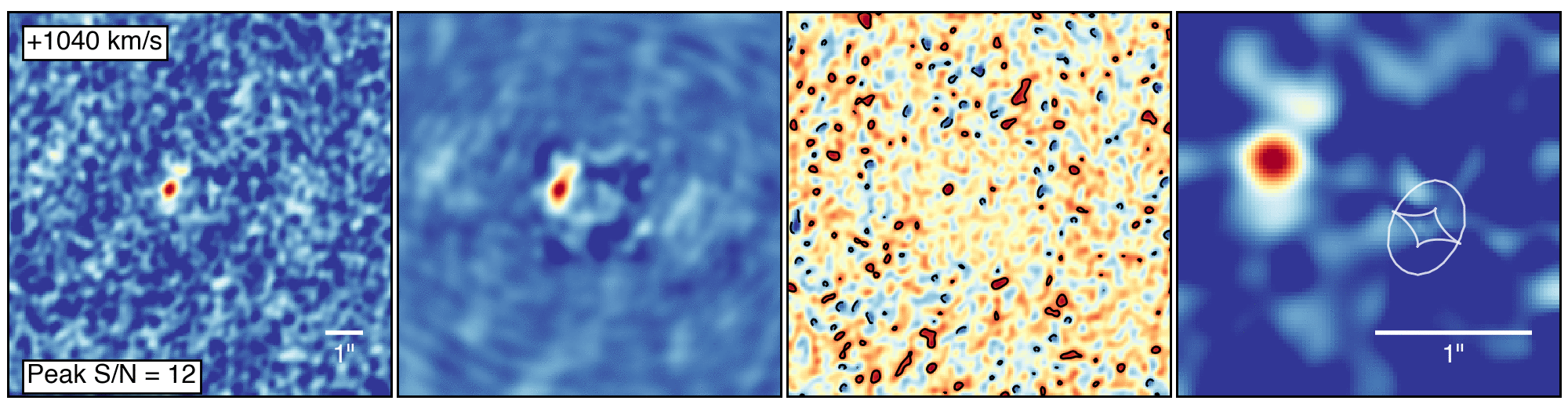
The galaxies that Marrone and his team studied, collectively known as SPT0311-58, were originally identified as a single source by the South Pole Telescope. These first observations indicated that this object was very distant and glowing brightly in infrared light, meaning that it was extremely dusty and likely going through a burst of star formation. Subsequent observations with ALMA revealed the distance and dual nature of the object, clearly resolving the pair of interacting galaxies.
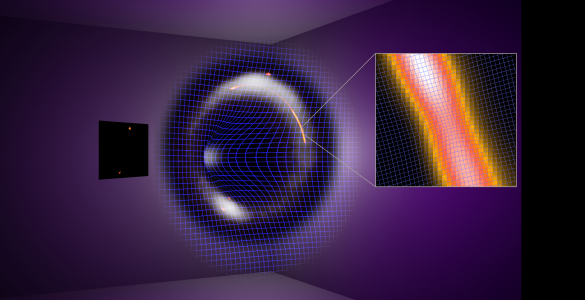
To make this observation, ALMA had some help from a gravitational lensGravitational LensThe effect when light from a distant object, such as a galaxy, is bent by the gravity of a massive object, such as another galaxy, before it reaches the Earth. If the two objects are perfectly aligned, the light from the distant object appears as a ring, to observers on Earth. This phenomenon is called an Einstein Ring, since its existence was predicted by Einstein in his theory of General Relativity. (see definition above), which provided an observing boost to the telescope. Gravitational lenses form when an intervening massive object, like a galaxy or galaxy cluster, bends the light from more distant galaxies. They do, however, distort the appearance of the object being studied, requiring sophisticated computer models to reconstruct the image as it would appear in its unaltered state.
This “de-lensing” process provided intriguing details about the galaxies, showing that the larger of the two is forming stars at a rate of 2,900 solar massSolar MassA solar mass, the calculated mass of our sun (332,946 times the mass of Earth). It is a standard unit of measure for extremely massive cosmic objects.es per year. It also contains about 270 billion times the mass of our sun in gas and nearly 3 billion times the mass of our sun in dust. “That’s a whopping large quantity of dust, considering the young age of the system,” noted Justin Spilker, a recent graduate of the University of Arizona and now a postdoctoral fellow at the University of Texas at Austin.
The astronomers determined that this galaxy’s rapid star formation was likely triggered by a close encounter with its slightly smaller companion, which already hosts about 35 billion solar masses of stars and is increasing its rate of starburst at the breakneck pace of 540 solar masses per year.
The researchers note that galaxies of this era are “messier” than the ones we see in the nearby universe. Their more jumbled shapes would be due to the vast stores of gas raining down on them and their ongoing interactions and mergers with their neighbors.
The new observations also allowed the researchers to infer the presence of a truly massive dark matter halo surrounding both galaxies. Dark matter provides the pull of gravity that causes the universe to collapse into structures (galaxies, groups and clusters of galaxies, etc.).
“If you want to see if a galaxy makes sense in our current understanding of cosmology, you want to look at the dark matter halo — the collapsed dark matter structure — in which it resides,” said Chris Hayward, associate research scientist at the Center for Computational Astrophysics at the Flatiron Institute in New York City. “Fortunately, we know very well the ratio between dark matter and normal matter in the universe, so we can estimate what the dark matter halo mass must be.”
By comparing their calculations with current cosmological predictions, the researchers found that this halo is one of the most massive that should exist at that time.
“There are more galaxies discovered with the South Pole Telescope that we’re following up on,” said Joaquin Vieira of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, “and there is a lot more survey data that we are just starting to analyze. Our hope is to find more objects like this, possibly even more distant ones, to better understand this population of extreme dusty galaxies and especially their relation to the bulk population of galaxies at this epoch.”
“In any case, our next round of ALMA observations should help us understand how quickly these galaxies came together and improve our understanding of massive galaxy formation during reionization,” added Marrone.
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory is a facility of the National Science Foundation, operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc.
# # #
This research is presented in a paper titled “’Galaxy growth in a massive halo in the first billion years of cosmic history,” by D. Marrone, et al., which appears in Advance Online Publication for Nature. [http://www.nature.com/nature].
The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an international astronomy facility, is a partnership of the European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO), the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) and the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) of Japan in cooperation with the Republic of Chile. ALMA is funded by ESO on behalf of its Member States, by NSF in cooperation with the National Research Council of Canada (NRC) and the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) in Taiwan and by NINS in cooperation with the Academia Sinica (AS) in Taiwan and the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI).
ALMA construction and operations are led by ESO on behalf of its Member States; by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), managed by Associated Universities, Inc. (AUI), on behalf of North America; and by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ) on behalf of East Asia. The Joint ALMA Observatory (JAO) provides the unified leadership and management of the construction, commissioning and operation of ALMA.
Contact:
Charles Blue, Public Information Officer
(434) 296-0314; cblue@nrao.edu