The U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO) took the Observatory’s new portable Starlab planetarium on…

Danielle Rowland, Senior Broadening Participation Programs Manager, was recently appointed as Native Nations Engagement Lead of the U.S. National…

Nestled in the woods near North Liberty, Iowa, this antenna can’t be seen from the road, but is occasionally…

Are you planning on viewing the solar eclipse on April 8, 2024? Please make sure you are doing so…

Transit Method When a planet passes directly between a star and its observer, it dims the star’s light by…

SuperKnova is a project to provide learning opportunities in radio technology for students in a way that is inclusive…

Three million years ago the fault regions of the Sierra Nevada and White Mountains began their thunderous rise. Their…
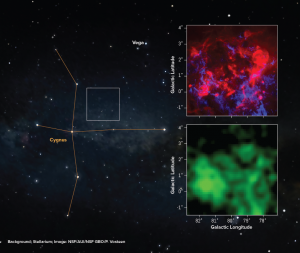
#RADIOIMAGEOFTHEWEEK
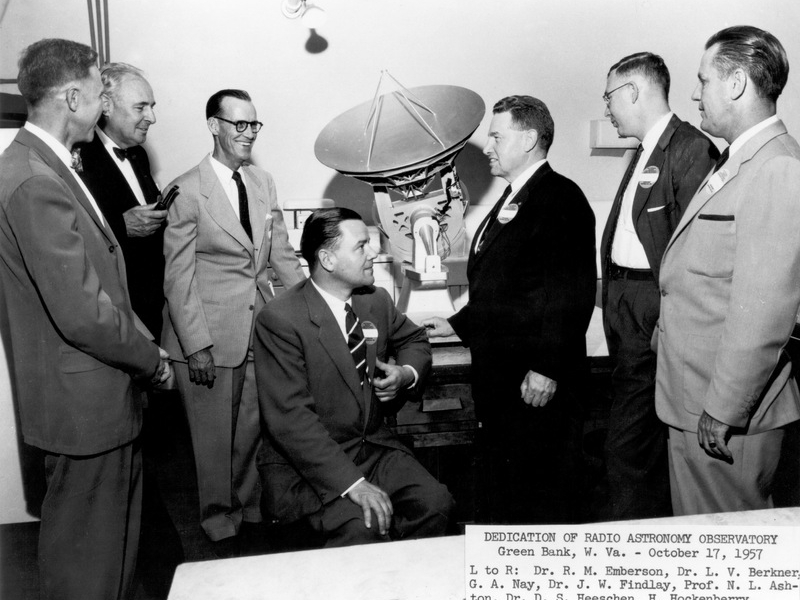

NRAO Dedication, 17 October 1957
Dedication of NRAO, 17 October 1957. From left: Richard M. Emberson, Lloyd V. Berkner, G. A. Nay, John W. Findlay, Ned L. Ashton, David S. Heeschen, H. Hockenberry, with model of 140 Foot TelescopeNRAO Making Waves
Announcements and Achievements
-
NSF NRAO Very Large Array to Host Fall Open House October 11
The U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO) invites the public to the U.S. National Science Foundation Very Large Array (NSF VLA) for its annual Fall Open House on Saturday, October 11, 2025, from 9:00 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. This free, family-friendly event offers a rare chance to explore one of the world’s most iconic astronomical observatories through guided tours, talks by experts, hands-on learning activities, and more.
-
National Radio Astronomy Observatory Announces Bipartisan Capital Outlay Funding for Next Generation Learning Center
The U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO) is proud to announce a significant milestone in advancing STEAM education in rural New Mexico. This achievement is the result of dedicated advocacy by Socorro County and Associated Universities, Inc., whose efforts—combined with bipartisan support from state legislators and Governor Michelle Lujan Grisham—have secured $1.78 million in capital outlay funding for the Next Generation Learning Center at the U.S. National Science Foundation Very Large Array in Socorro County.
-
NSF’s ongoing technical coordination with satellite constellation operators
The U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) has announced a new coordination agreement with AST SpaceMobile to address the impact…
-
The Very Large Array to Host Fall Open House on October 12, 2024
The U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO) is thrilled to invite the public to the NSF Very Large Array (NSF VLA) Fall Open House on Saturday, October 12, 2024, from 9:00 am to 4:00 pm.

Different star types “live” and “die” in different ways based on how much matter they started with and if they were born with siblings nearby.