Instructions
To create your image:
- Choose an image to start.
- Turn on desired wavelengths to add them to your image.
- Choose a color for each wavelength.
- Adjust the brightness of each wavelength to bring out your favorite details.
- Choose the size you want and click "Generate".
- Follow the instructions below to save the image to your device.
Cosmic Coloring Compositor
Create your own mobile phone background, desktop background or social media banner with our colorful compositor
To fully grasp the nature of the universe, astronomers study all wavelengths of light – what scientists call the electromagnetic spectrum. A few of these wavelengths can be seen with the human eye. The longest visible wavelength is red and the shortest is violet. Other common colors of the spectrum, in order of decreasing wavelength, may be remembered by the mnemonic: ROY G BIV.
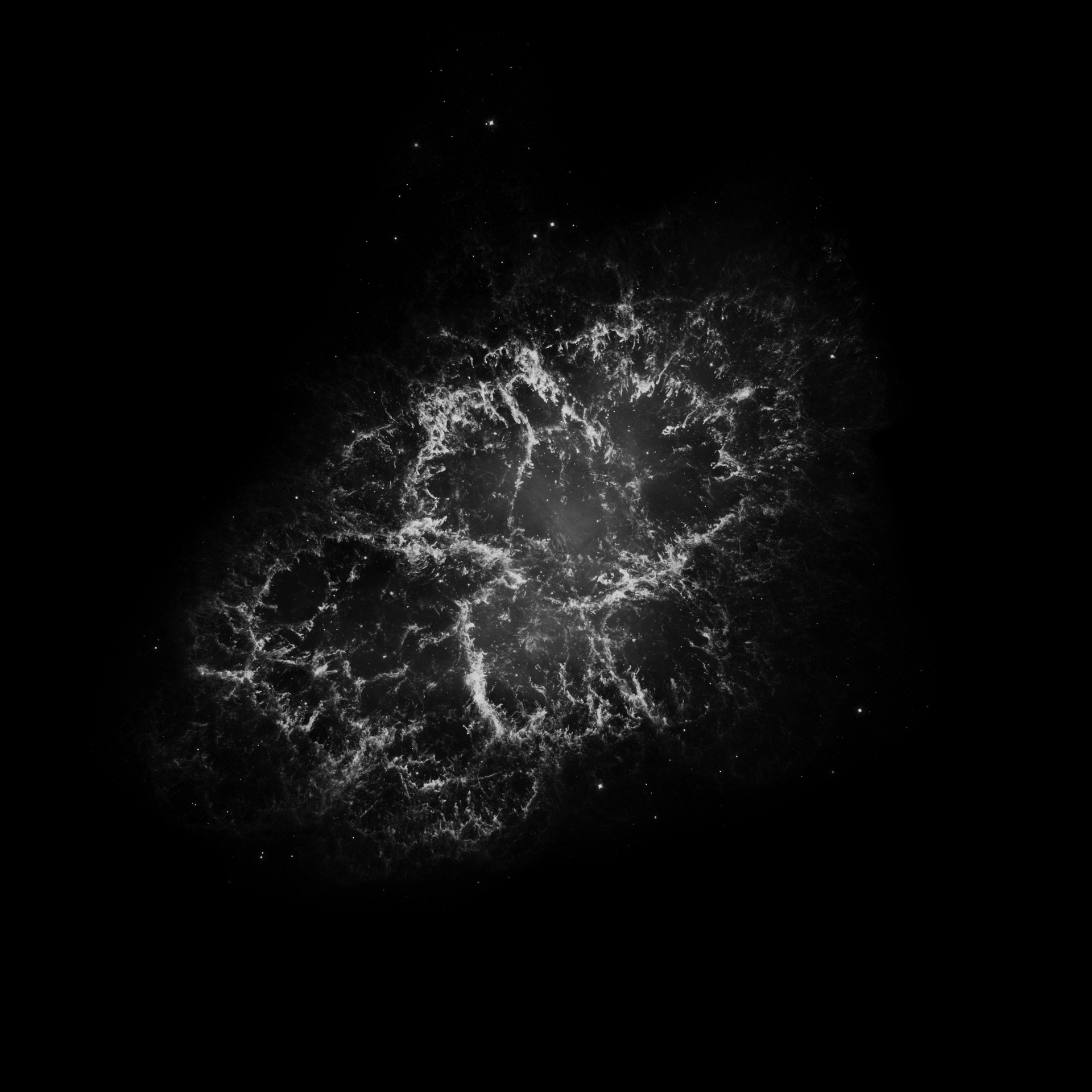
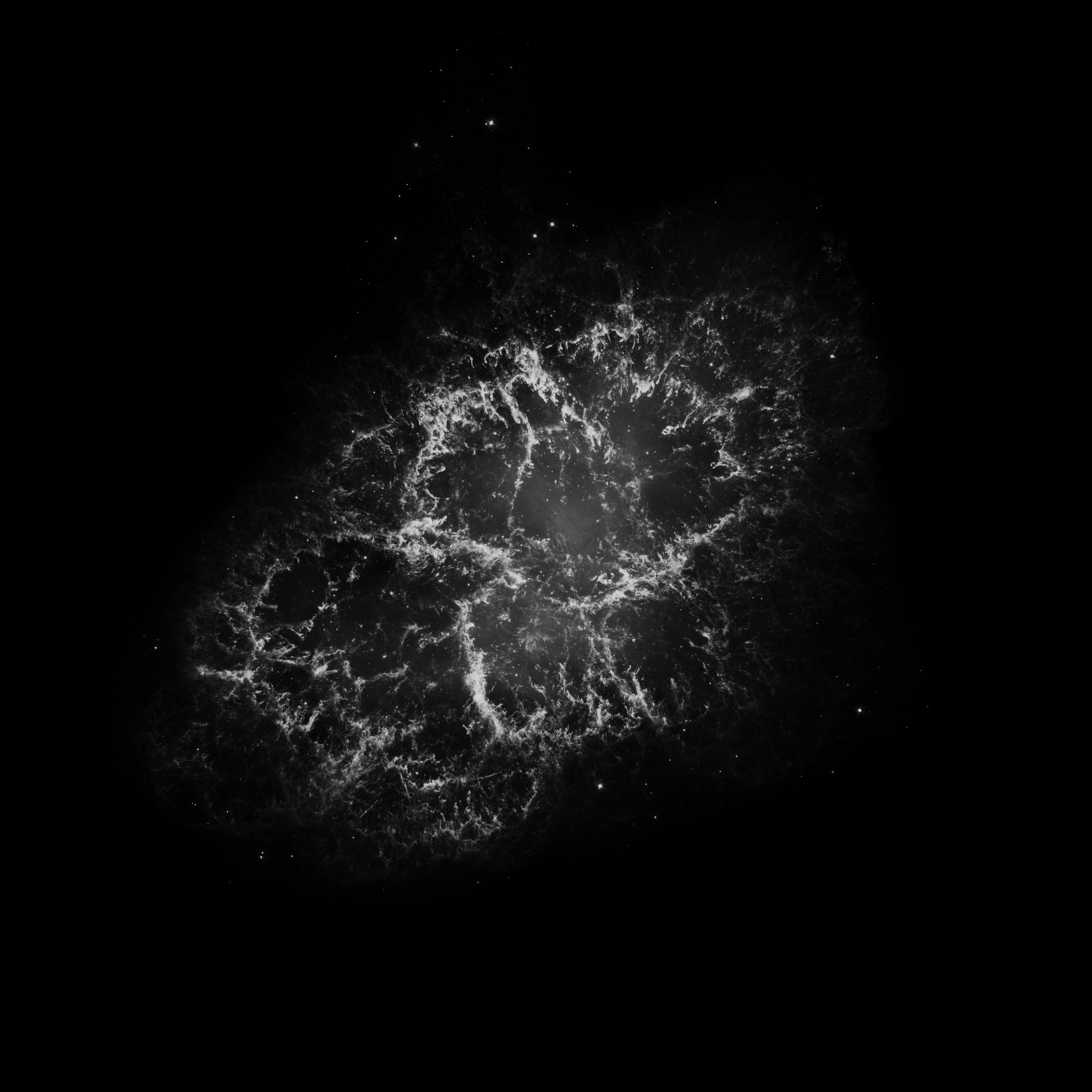
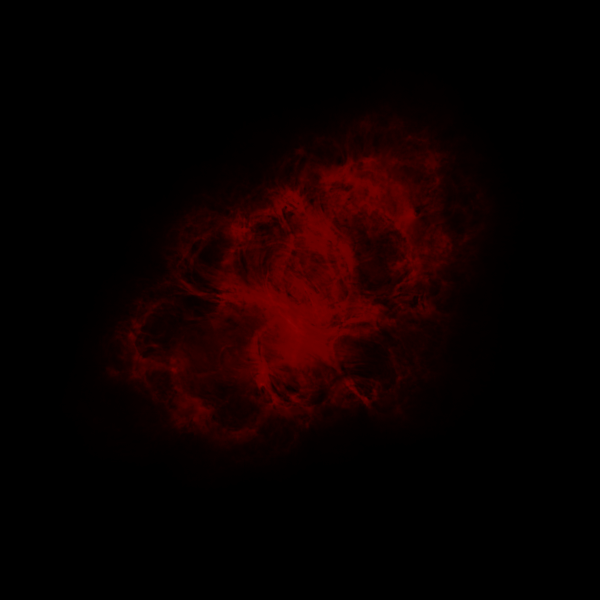
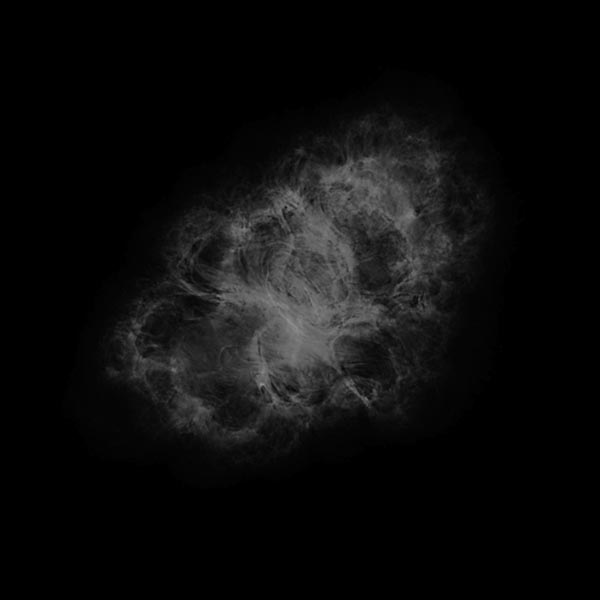
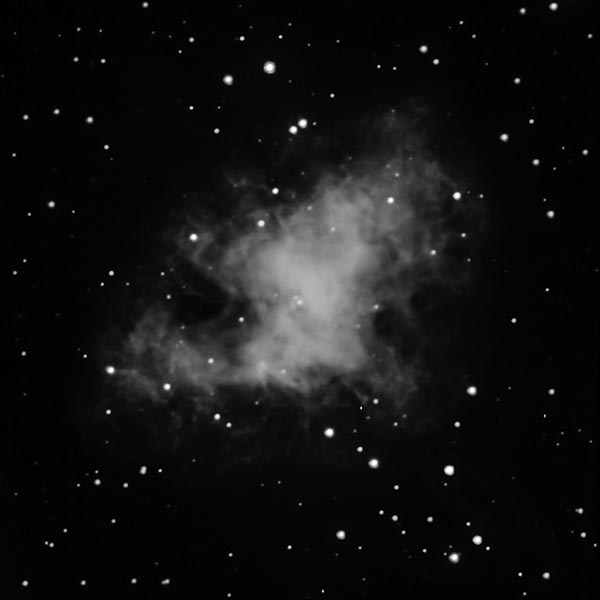
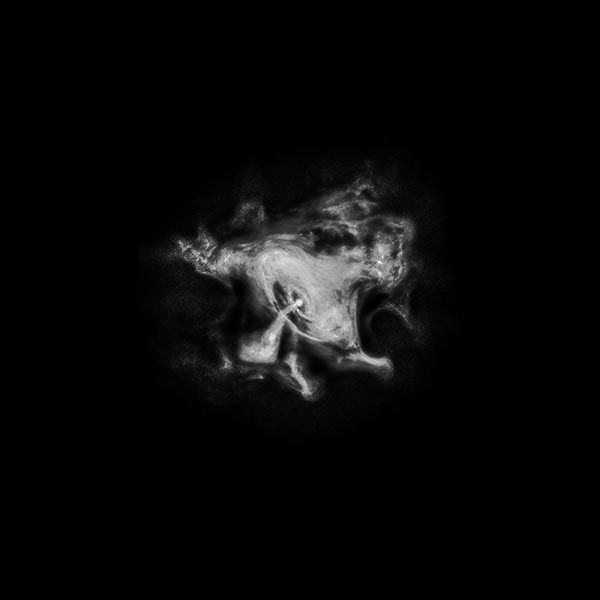
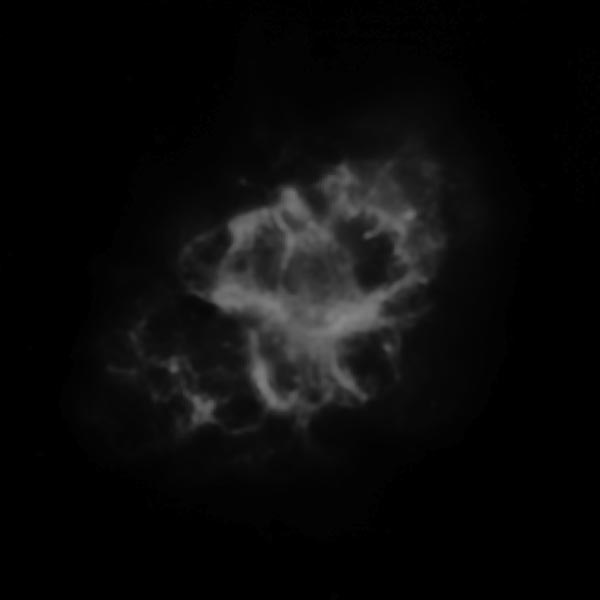
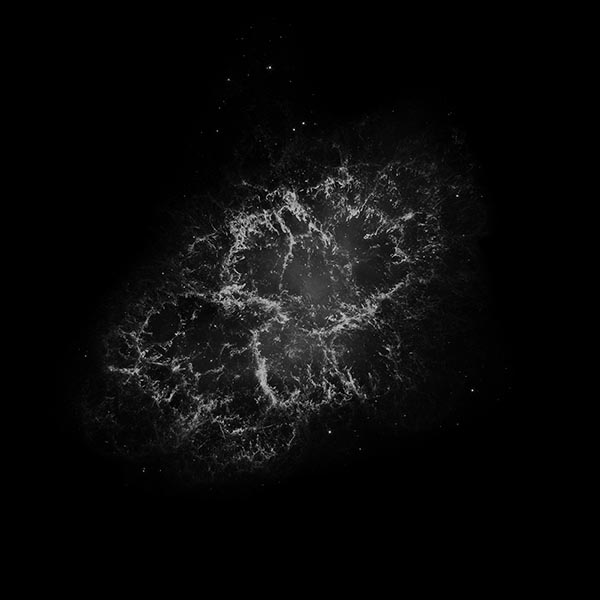
Astronomers have produced spectacular, multi-wavelength images such as the Crab Nebula – the remains of a supernova explosion – by combining data from telescopes spanning nearly the entire range of the electromagnetic spectrum, from the long radio waves seen by Very Large Array (VLA) to the shorter x-rays, on the opposite end of the spectrum, observed by NASA’s Chandra X-Ray Observatory.
Discover many amazing details of the invisible universe by changing the wavelengths of radio, infrared, ultraviolet, and X-ray to colors your eyes can recognize!
M1 Crab Nebula Learn More...




Saving Your Image