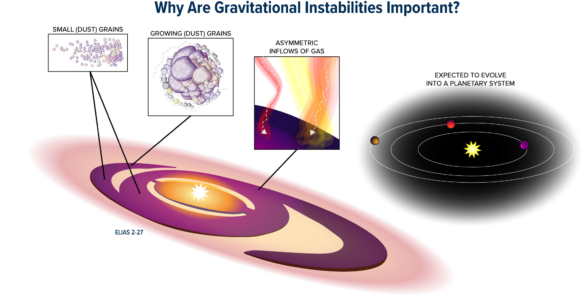
Cassiopeia A
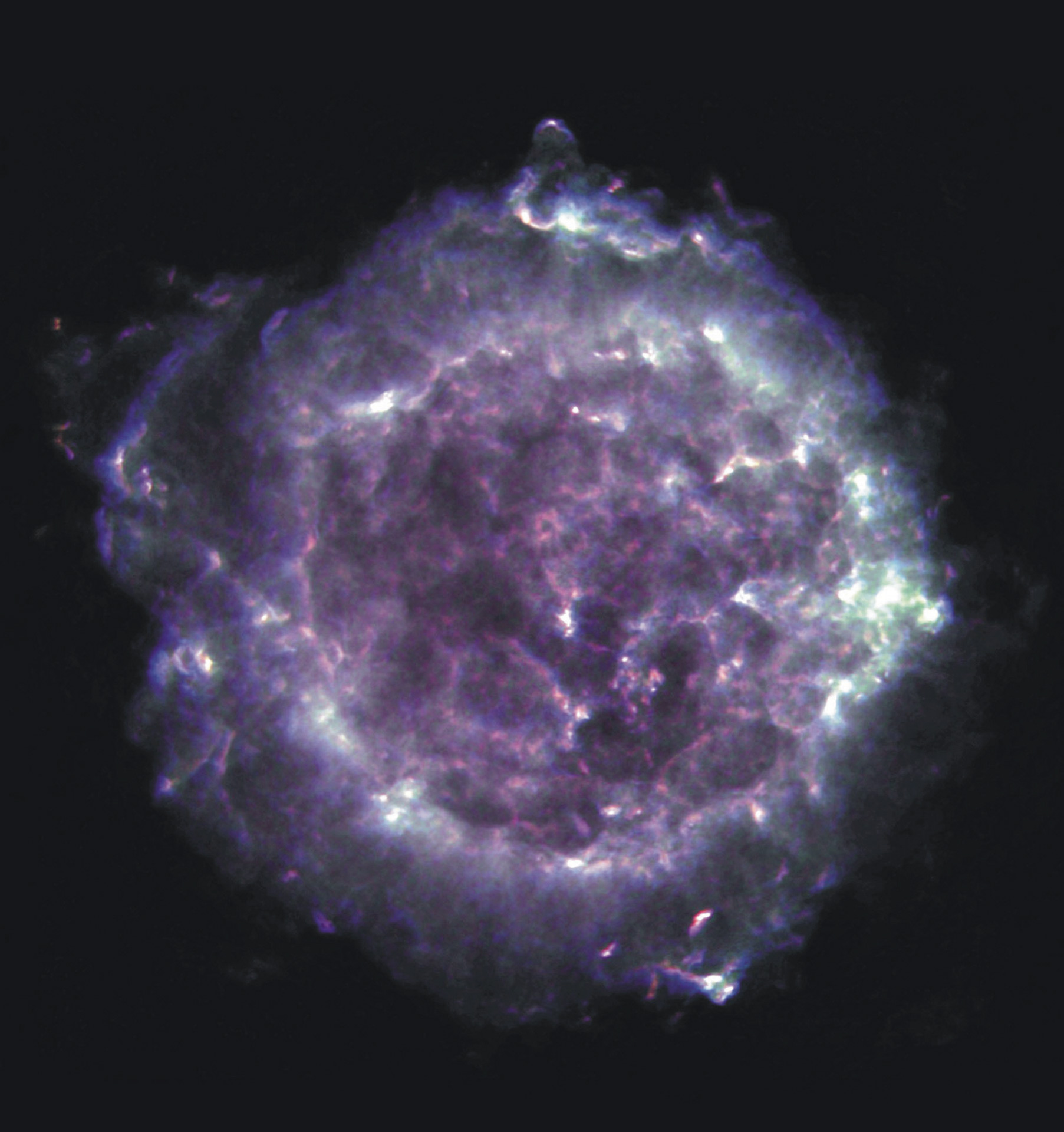
Cassiopeia A is the remnant of a supernova explosion that appeared in our sky over 300 years ago in our Galaxy, at a distance of about 11,000 light years from us. Its name is derived from the constellation in which it is seen: Cassiopeia, the Queen. A supernova is the explosion that occurs at the end of a massive star’s life; and Cassiopeia A is the expanding shell of material that remains from such an explosion. This radio image of Cassiopeia A was created with the National Science Foundation’s Very Large Array telescope in New Mexico. Cassiopeia A is one of the brightest radio sources in the sky, and has been a popular target of study for radio astronomers for decades. The material that was ejected from the supernova explosion can be seen in this image as bright filaments.
| Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Telescope | VLA |
| Band | L; C; X |
| Date | 1994-03-25 |
| Center | RA: 23:21:13, Dec: 58:32:35 |
| Field of View | 6 x 6 arcminutes |