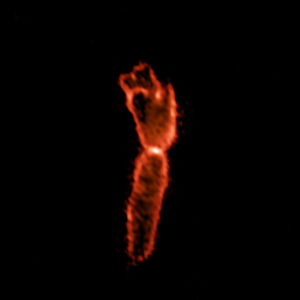
Astronomers using the National Science Foundation’s Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) have discovered new details that are helping them decipher the mystery of how giant radio-emitting structures are formed at the center of a cluster of galaxies. The scientists studied a cluster of thousands of galaxies more than 250 million light-years from Earth, named the Perseus Cluster after the constellation in which it appears. Embedded within the center, the Perseus Cluster hosts a pool of superfast particles that emit radio waves, creating a radio structure known as a “mini-halo.” Mini-haloes have been found in about 30 galaxy clusters, but the halo in the Perseus Cluster is the largest known, about 1.3 million light-years in diameter, or 10 times the size of our Milky Way Galaxy. Radio emission in red; optical in white.

The Ultra-Cold Outflow of the Boomerang Nebula
The Boomerang Nebula, a pre-planetary nebula produced by a dying star. ALMA observations show the hourglass-shaped outflow, which is embedded inside a roughly round ultra-cold outflow. The hourglass outflow stretches more than three trillion kilometers from end to end (about 21,000 times the distance from the Sun to the Earth), and is the result of a jet that is being fired by the central star, sweeping up the inner regions of the ultra-cold outflow like a snow-plow. The ultra-cold outflow is about 10 times bigger.

ALMA Returns to Boomerang Nebula, ‘Coldest Object in the Universe’
Composite image of the Boomerang Nebula, a pre-planetary nebula produced by a dying star. ALMA observations (orange) showing the hourglass-shaped outflow, which is embedded inside a roughly round ultra-cold outflow. The hourglass outflow stretches more than three trillion kilometers from end to end (about 21,000 times the distance from the Sun to the Earth), and is the result of a jet that is being fired by the central star, sweeping up the inner regions of the ultra-cold outflow like a snow-plow. The ultra-cold outflow is about 10 times bigger. The ALMA data are shown on top of an image from the Hubble Space Telescope (blue).

VLA Reveals New Object Near Supermassive Black Hole in Famous Galaxy
VLA radio images (orange) of central region of Cygnus A, overlaid on Hubble Space Telescope image, from 1989 and 2015. Animated GIF.

New Companion Object Found Near Cygnus A’s Supermassive Black Hole
Pointing the National Science Foundation’s Very Large Array (VLA) at a famous galaxy for the first time in two decades, a team of astronomers got a big surprise, finding that a bright new object had appeared near the galaxy’s core. The object, the scientists concluded, is either a very rare type of supernova explosion or, more likely, an outburst from a second supermassive black hole closely orbiting the galaxy’s primary, central supermassive black hole.
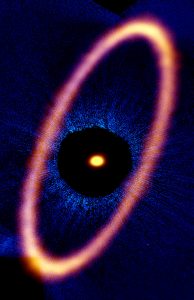
ALMA Eyes Icy Ring around Young Planetary System
Composite image of the Fomalhaut star system. The ALMA data, shown in orange, reveal the distant and eccentric debris disk in never-before-seen detail. The central dot is the unresolved emission from the star, which is about twice the mass of our sun. Optical data from the Hubble Space Telescope is in blue; the dark region is a coronagraphic mask, which filtered out the otherwise overwhelming light of the central star.





