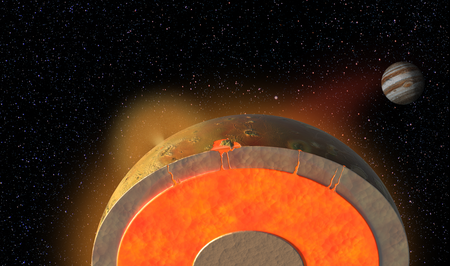
Jupiter’s moon Io is the most volcanically active place in the solar system. During its 1.8-day orbit, this moon is gravitationally squeezed by Jupiter, leading to volcanic eruptions larger than any on Earth today.
Io, Europa, and Ganymede are in an orbital configuration known as a Laplace resonance: for every orbit of Ganymede (the farthest of the three from Jupiter), Europa completes exactly two orbits, and Io completes exactly four. In this configuration, the moons pull on each other gravitationally in such a way that they are forced into elliptical, rather than round, orbits. Such orbits allow Jupiter’s gravity to heat the moons’ interiors, causing Io’s volcanism and adding heat to the subsurface liquid ocean on icy Europa.
How long has Io been experiencing volcanic upheaval? In other words, how long have Jupiter’s moons been in this configuration?
To discover the answer, researchers utilized the ALMA (Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array) telescope in Chile—a telescope that is itself surrounded by volcanoes—to measure sulfur isotopes on Io.