Latest NRAO News
News is managed by NRAO News & Public Information. Questions about News? Have a story to share? Want to interview a scientist or create new media about our telescopes?

Astronomers using radio telescopes from around the world have discovered a spinning neutron star with a superpowerful magnetic field — called a magnetar — doing things no magnetar has been seen to do before.
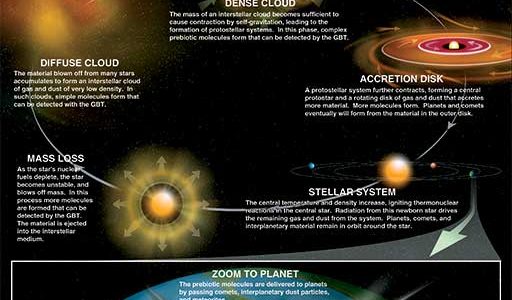
In just two years of work, an international research team has discovered eight new complex, biologically-significant molecules in interstellar space using the National Science Foundation’s Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope (GBT) in West Virginia.
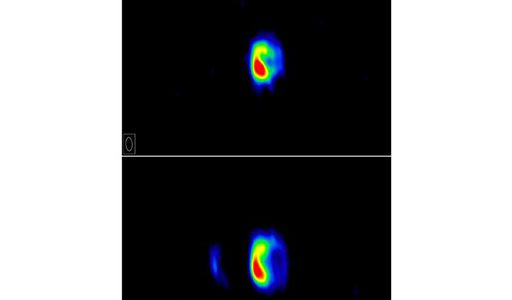
A powerful thermonuclear explosion on a dense white-dwarf star last February has given astronomers their best look yet at the early stages of such explosions, called novae, and also is giving them tantalizing new clues about the workings of bigger explosions, called supernovae, that are used to measure the Universe.

One of the pioneers of radio astronomy tells her story of the formative years of that science in a memoir published by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory.

Astronomers using the National Science Foundation’s Very Long Baseline Array radio telescope have found the closest pair of supermassive black holes ever discovered in the Universe — a duo of monsters that together are more than 150 million times more massive than the Sun and closer together than the Earth and the bright star Vega.
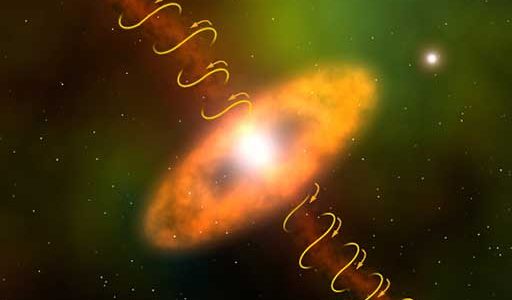
Molecules spewed outward from a dying star are confined into narrow jets by a tightly-wound magnetic field, according to astronomers who used the National Science Foundation’s Very Long Baseline Array radio telescope to study an old star about 8,500 light-years from Earth.





