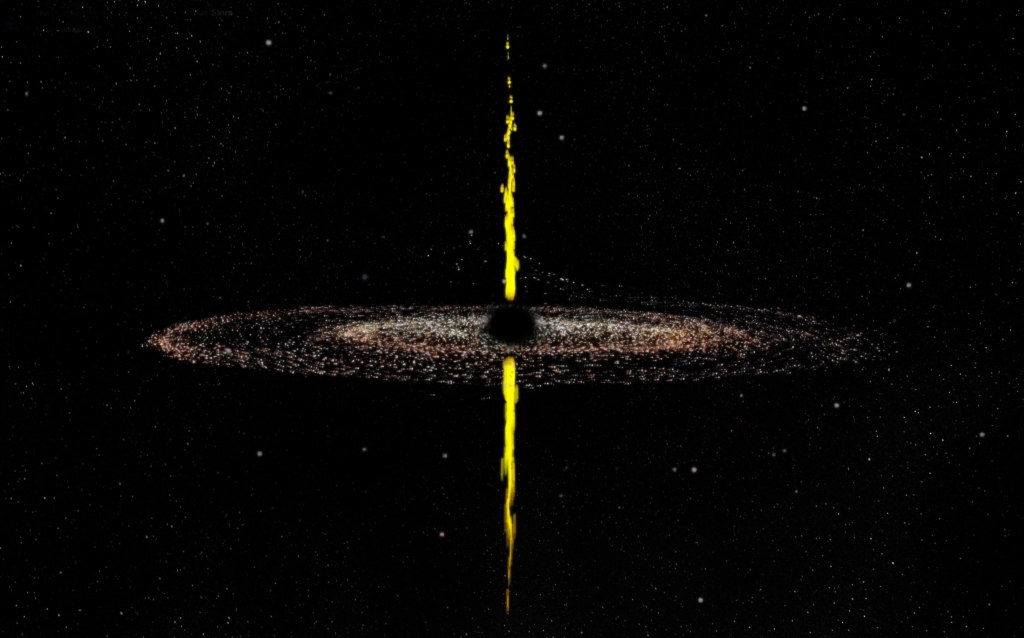
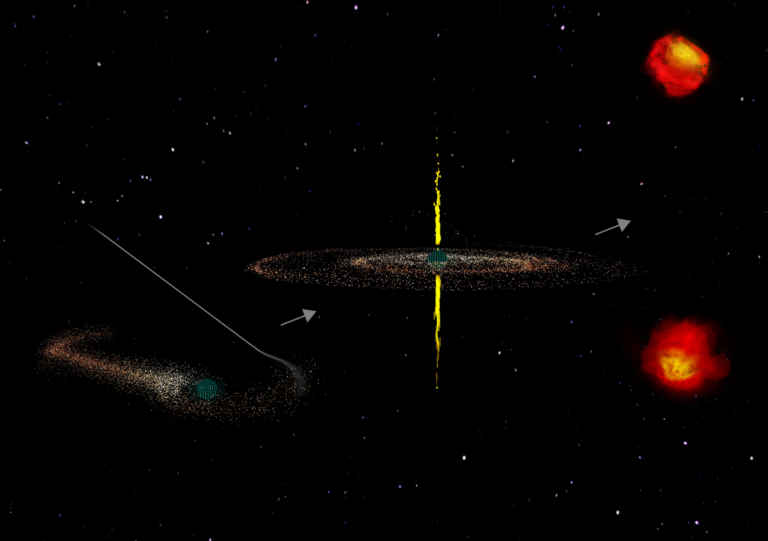
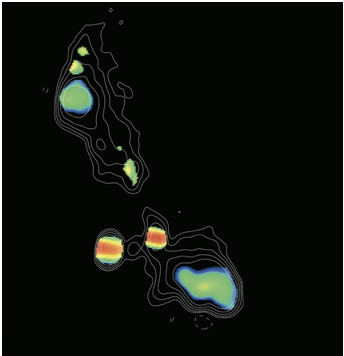
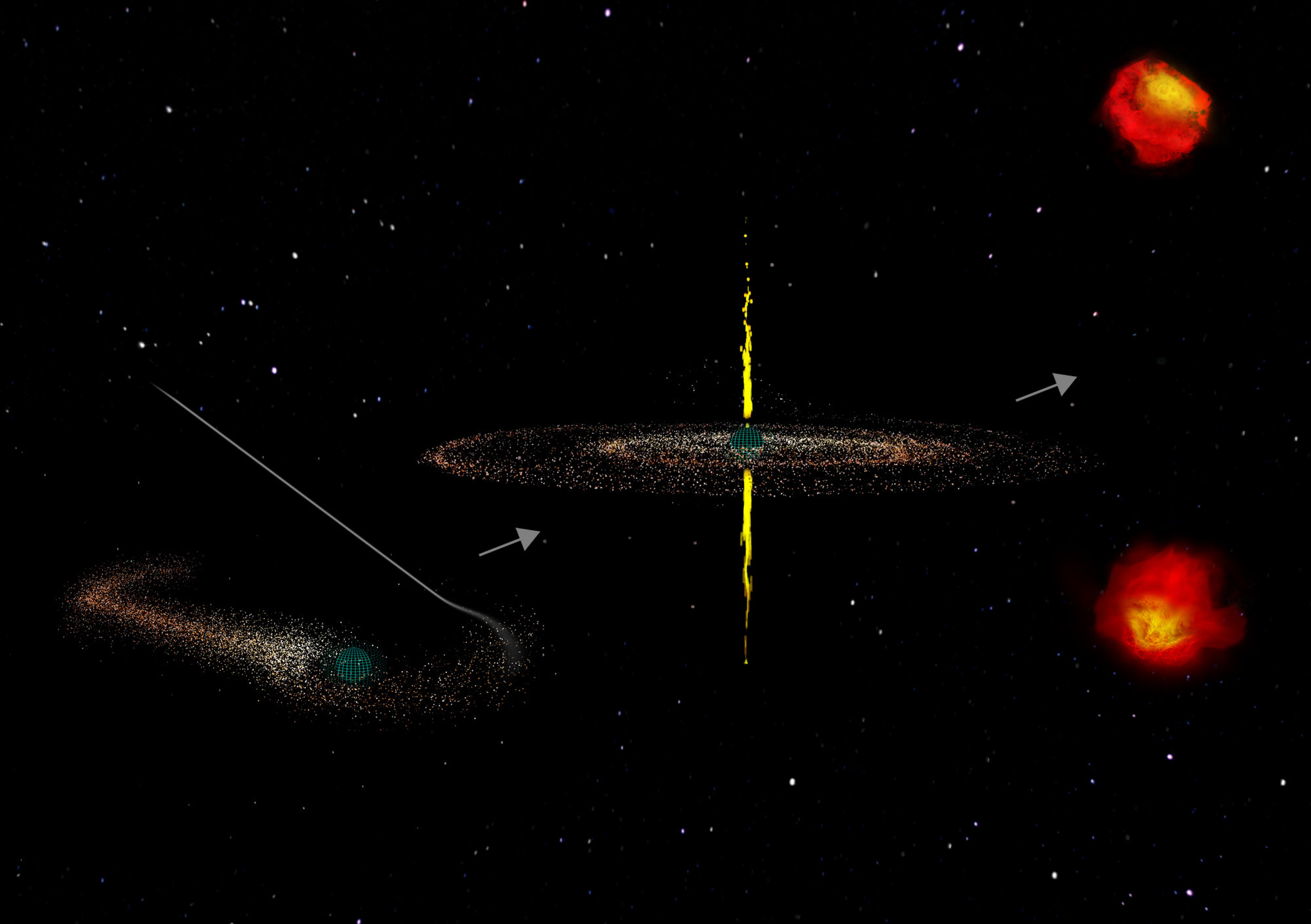
Compact Symmetric Objects (CSOs) have long puzzled astronomers with their unique characteristics. These active galaxies harbor supermassive black holes that emit powerful jets traveling at near-light speeds in opposite directions. However, unlike their counterparts in other galaxies, these jets remain compact, not extending out to great distances as expected. For decades, scientists presumed that CSOs were youthful entities, with their jets destined to expand over time.
New findings, published in three papers in The Astrophysical Journal, challenge this notion. The Caltech-led team, spearheaded by Anthony (Tony) Readhead, Robinson Professor of Astronomy, Emeritus, discovered that CSOs have relatively short lifespans. Through an exhaustive review of literature and observations, the team identified over 3,000 CSO candidates, confirming 64 as authentic CSOs and recognizing 15 new candidates. These objects were previously observed by the U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO)’s Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA), renowned for its unparalleled resolution.
The studies, funded by NSF, NASA, Caltech, and the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy in Bonn, Germany, mark a significant step forward in understanding the dynamic processes shaping our universe. Read the full Caltech release HERE and view NRAO’s scientific visualization animation HERE.
About NRAO
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) is a facility of the U.S. National Science Foundation, operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc.
For media inquiries or further information, please contact:
NRAO Media Contact
Corrina C. Jaramillo Feldman
Public Information Officer – New Mexico
VLA, VLBA, ngVLA
Tel: +1 505-366-7267
cfeldman@nrao.edu