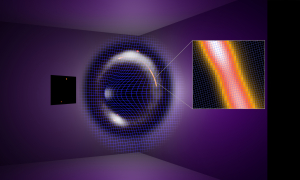
An international research team, using a worldwide network of radio telescopes, including the U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO) VLBA and GBT, has detected an enigmatic dark object with a mass about one million times that of our Sun without observing any emitted light. This is the lowest mass dark object ever detected at a cosmological distance using only its gravitational influence, marking a major milestone in the quest to unravel the nature of dark matter.

National Radio Astronomy Observatory to Outfit the VLBA with New Ultra Wideband Receivers
The U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO) has begun a major upgrade to the NSF Very Long Baseline Array (NSF VLBA) with the development and installation of state-of-the-art ultra wideband receivers capable of operating across the frequency range of 8 to 40 gigahertz (GHz). This new technology, first prototyped by NRAO in collaboration with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), and tested on the NSF VLBA’s Owens Valley station, promises to significantly expand the scientific capabilities of the NSF VLBA.

NSF NRAO Achieves First Successful Observations with New NSF VLBA Digital Architecture
The new NSF VLBA New Digital Architecture (VNDA) produced its first fringes and subsequent images in January 2025, demonstrating the successful implementation of next-generation technology that will enhance the NSF VLBA’s scientific capabilities for years to come.

Astronomers Catch Unprecedented Features at Brink of Active Black Hole
International teams of astronomers monitoring a supermassive black hole in the heart of a distant galaxy have detected features never seen before using data from NASA missions and other facilities including the National Science Foundation (NSF) National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO) Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA).

Astronomers Detect Earliest and Most Distant Blazar in the Universe
A groundbreaking discovery has revealed the presence of a blazar—a supermassive black hole with a jet pointed directly at Earth—at an extraordinary redshift of 7.0. The object, designated VLASS J041009.05−013919.88 (J0410−0139), is the most distant blazar ever identified, providing a rare glimpse into the epoch of reionization when the universe was less than 800 million years old. This discovery challenges existing models of black hole and galaxy formation in the early cosmos.

Precision Measurements Offer Clues to Magnetar’s Cosmic Origin
An international team of astronomers have used a powerful array of radio telescopes to discover new insights about a magnetar that’s only a few hundred years old. By capturing precise measurements of the magnetar’s position and velocity, new clues emerge regarding its developmental path.





