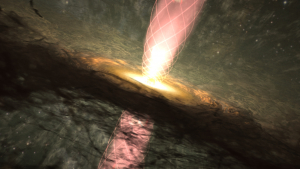
Using the U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy’s Very Long Baseline Array (NSF NRAO VLBA), an international team of astronomers has solved a decade-long puzzle about one of the brightest cosmic neutrino sources in the sky. Their findings, published today in Astronomy & Astrophysics Letters, reveal that the blazar PKS 1424+240 – dubbed the “Eye of Sauron” for its striking appearance – points its powerful jet almost directly at Earth, creating an extreme cosmic lighthouse effect.
Astronomers Catch Supermassive Black Hole in the Act of “Waking Up”
Astronomers using the U.S. National Science Foundation’s Very Long Baseline Array (NSF VLBA) and U.S. National Science Foundation’s Very Large Array (NSF VLA) have caught a supermassive black hole in the act of awakening from a long slumber, providing an unprecedented glimpse into the earliest stages of black hole activity.
Astronomers Catch Unprecedented Features at Brink of Active Black Hole
International teams of astronomers monitoring a supermassive black hole in the heart of a distant galaxy have detected features never seen before using data from NASA missions and other facilities including the National Science Foundation (NSF) National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO) Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA).
Helical Magnetic Fields: A Universal Mechanism for Jet Collimation?
New observations from the National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory’s (NSF NRAO) Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (NSF VLA) provide compelling evidence supporting a universal mechanism for the collimation of astrophysical jets, regardless of their origin. A new study, published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters, reveals the presence of a helical magnetic field within the HH 80-81 protostellar jet, a finding that mirrors similar structures observed in jets emanating from supermassive black holes.
Astronomers Detect Earliest and Most Distant Blazar in the Universe
A groundbreaking discovery has revealed the presence of a blazar—a supermassive black hole with a jet pointed directly at Earth—at an extraordinary redshift of 7.0. The object, designated VLASS J041009.05−013919.88 (J0410−0139), is the most distant blazar ever identified, providing a rare glimpse into the epoch of reionization when the universe was less than 800 million years old. This discovery challenges existing models of black hole and galaxy formation in the early cosmos.
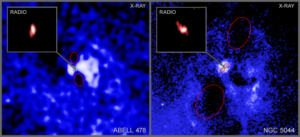
Spotted: ‘Death Star’ Black Holes in Action
Huge black holes are firing powerful beams of particles into space — and then changing their aim to fire at new targets.