Latest NRAO News
News is managed by NRAO News & Public Information. Questions about News? Have a story to share? Want to interview a scientist or create new media about our telescopes?
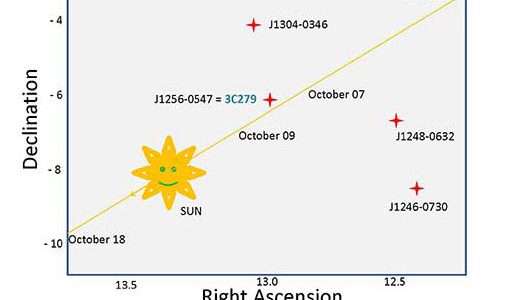
Scientists using a continent-wide array of radio telescopes have made an extremely precise measurement of the curvature of space caused by the Sun’s gravity, and their technique promises a major contribution to a frontier area of basic physics.
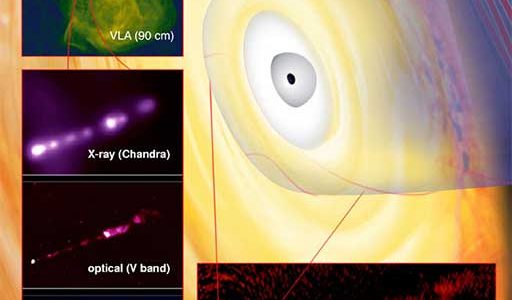
Using a worldwide combination of diverse telescopes, astronomers have discovered that a giant galaxy’s bursts of very high energy gamma rays are coming from a region very close to the supermassive black hole at its core. The discovery provides important new information about the mysterious workings of the powerful engines in the centers of innumerable galaxies throughout the Universe.

Radio astronomers have directly measured the distance to a faraway galaxy, providing a valuable yardstick for calibrating large astronomical distances and demonstrating a vital method that could help determine the elusive nature of the mysterious Dark Energy that pervades the Universe.
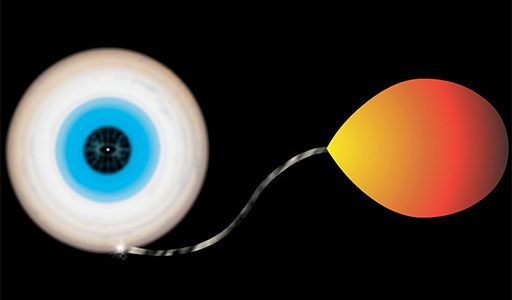
Astronomers have discovered a unique double-star system that represents a missing link stage in what they believe is the birth process of the most rapidly-spinning stars in the Universe — millisecond pulsars.
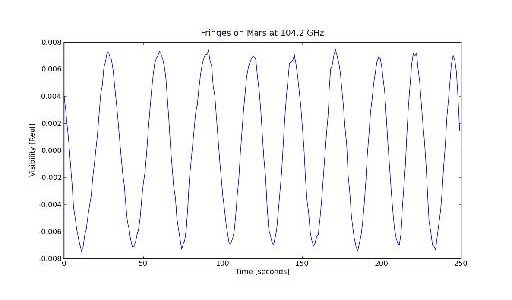
The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array, an immense international telescope project under construction in northern Chile, reached a major milestone on April 30, when two ALMA antennas were linked together as an integrated system to observe an astronomical object for the first time.
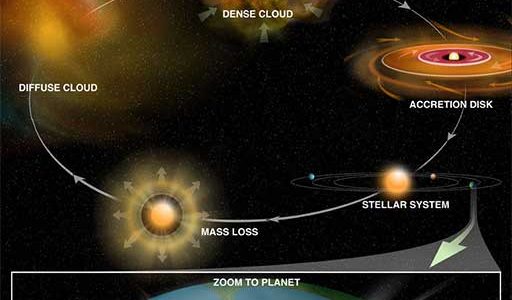
Processes that laid the foundation for life on Earth — star and planet formation and the production of complex organic molecules in interstellar space — are yielding their secrets to astronomers armed with powerful new research tools, and even better tools soon will be available.





