Latest NRAO News
News is managed by NRAO News & Public Information. Questions about News? Have a story to share? Want to interview a scientist or create new media about our telescopes?

AUI and NRAO have announced the recipients of the 2023 AUI Board of Trustees NAC Bridge Scholarship Award, which recognizes the academic accomplishments of National Astronomy Consortium (NAC) alums and assists them in the transition from undergraduate to graduate programs.

Fast radio bursts are powerful flashes of light that shine for only milliseconds. Join our host Summer Ash of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory as she talks about how astronomers study these mysterious bursts, and what might be causing them.

NANOGrav’s most recent dataset offers compelling evidence for gravitational waves with oscillations of years to decades. These waves are thought to arise from orbiting pairs of the most massive black holes throughout the Universe: billions of times more massive than the Sun, with sizes larger than the distance between the Earth and the Sun.
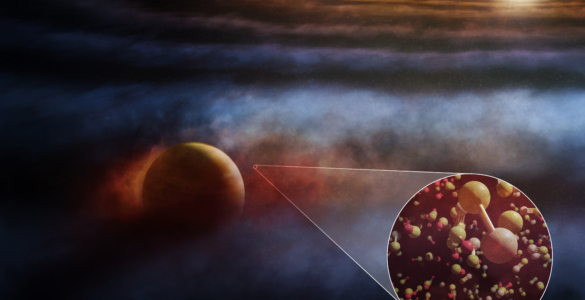
Scientists using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) to study the protoplanetary disk around a young star have discovered the most compelling chemical evidence to date of the formation of protoplanets. The discovery will provide astronomers with an alternate method for detecting and characterizing protoplanets when direct observations or imaging are not possible.

The NRAO has made a visible change to our logo for Pride month, because we want to send the clear message that NRAO values our current and future LGBTQIA+ colleagues, friends, and family members. We send this same message internally by taking seriously our obligation to create and maintain an environment that is safe, secure, and welcoming.
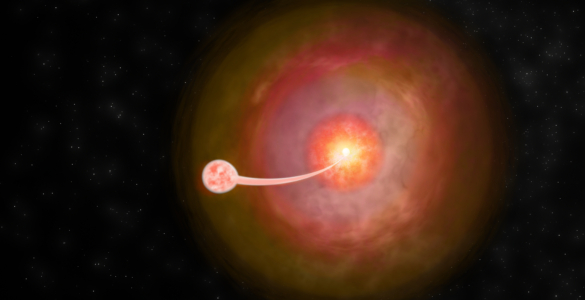
While studying classical novae using the National Radio Astronomy Observatory’s Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA), a graduate researcher uncovered evidence the objects may have been erroneously typecast as simple. The new observations detected non-thermal emission from a classical nova with a dwarf companion.





