Latest NRAO News
News is managed by NRAO News & Public Information. Questions about News? Have a story to share? Want to interview a scientist or create new media about our telescopes?
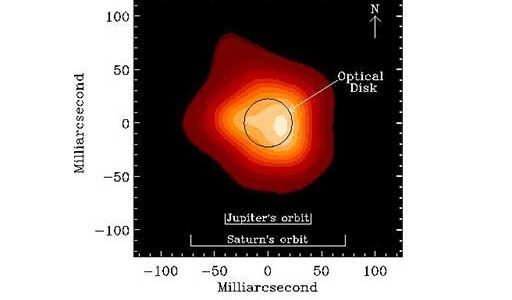
A team of astronomers says that observations with the National Science Foundation’s Very Large Array radio telescope show that a neighboring bloated star has giant convective plumes propelling gas from its surface up into the star’s atmosphere.

A team of astronomers using a pair of National Science Foundation radio telescopes has made the first measurements of the size and expansion of a mysterious, intense fireball resulting from a cosmic gamma ray burst last May.
Marking an important new milestone in radio astronomy history, scientists at the National Radio Astronomy Observatory in Socorro, New Mexico, have made the first images using a radio telescope antenna in space.

Radio astronomers revealed that the first gamma-ray burster ever detected at radio wavelengths has surprised them by its erratic behavior.

Astronomers have used the National Science Foundation’s Very Large Array radio telescope to make the first detection of radio emission from a cosmic gamma-ray burst.

A claim that the universe has a preferred direction is not supported by recent observational evidence, according to three astronomers who analyzed data from the Very Large Array radio telescope in New Mexico and the WM Keck Telescope in Hawaii.

The discovery of microquasars within our own Milky Way Galaxy has won two astronomers a prize from the High Energy Astrophysics Division of the American Astronomical Society.
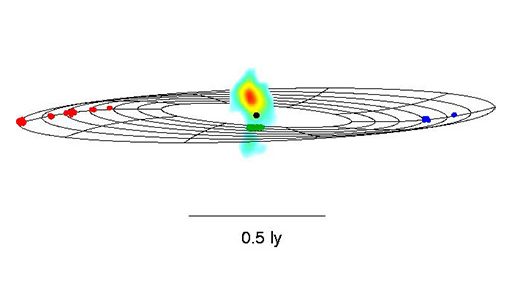
An extraordinary cosmic laboratory 21 million light-years away is providing radio astronomers their best opportunity yet to decipher the mysteries of the ultra-powerful engines at the hearts of many galaxies and quasars.

A VLA upgrade proposes an essentially new instrument, created from two existing instruments, with power and capability far exceeding that of either one alone.

Do nearby stars have planetary systems like our own? How do such systems evolve? How common are such systems? Proposed radio observatories operating at millimeter wavelengths could start answering these questions within the next 6-10 years, according to scientists at the National Radio Astronomy Observatory.





