Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system. It is also the brightest planet at radio frequencies. While radio astronomy often focuses on more distant objects such as nebulae and galaxies, the radio astronomy of planets begins with Jupiter.
While other planets in our solar system emit radio light, Jupiter is by far the most radio bright. When charged particles in space interact with Jupiter’s magnetic field, they emit radio light through a process known as synchrotron radiation. The first radio observation of Jupiter was made by Bernard Burke and Kenneth Franklin in 1955. They weren’t expecting such a signal, so they initially thought it was the radio noise of a farm-hand driving home. But subsequent observations showed the signal was Jovian in origin.
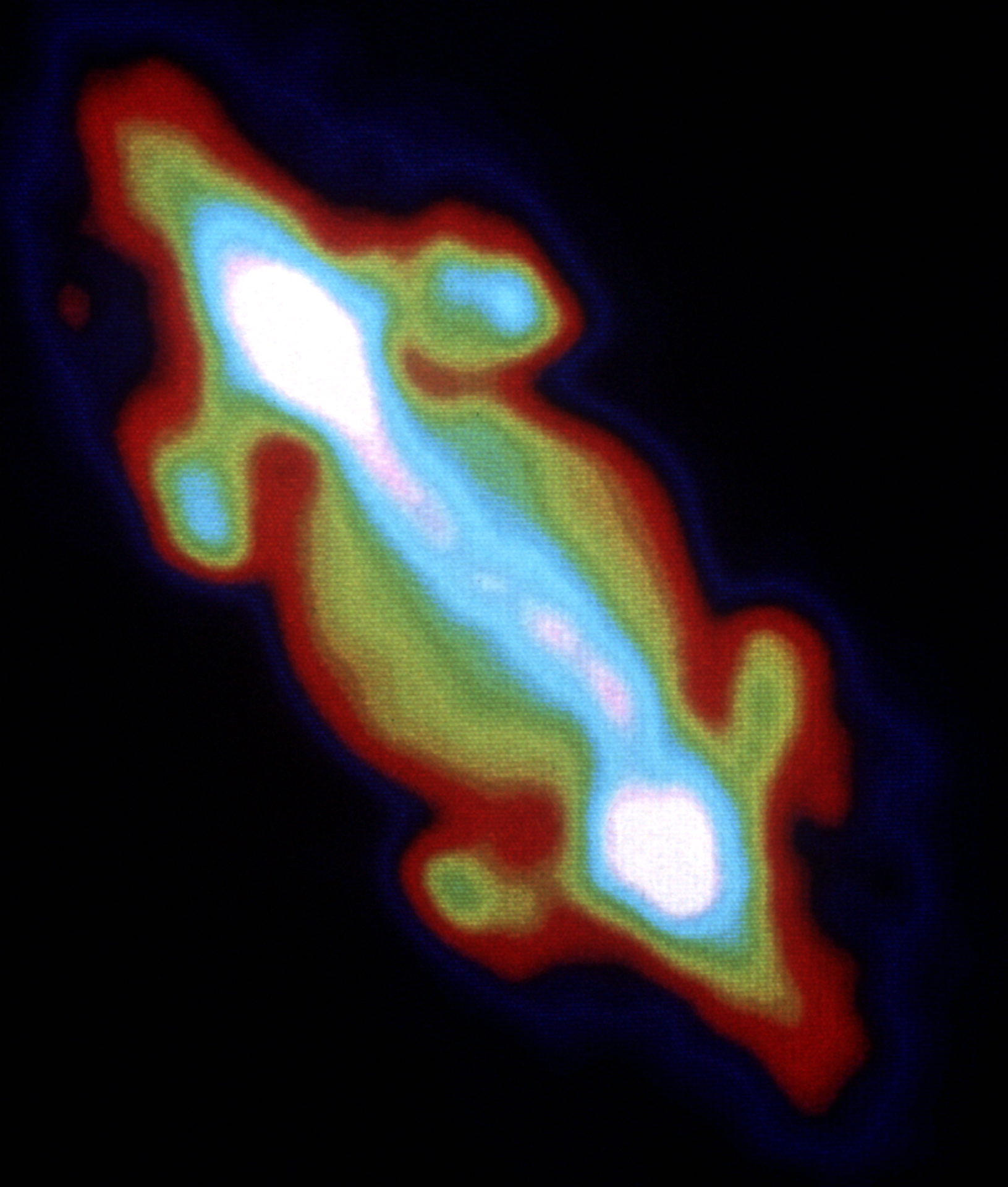
In addition to its synchrotron emissions, Jupiter also gives off radio light due to thermal emissions. These fainter emissions were first mapped by the Very Large Array (VLA). The VLA’s antennas can work together in a wide configuration to capture faint and high-resolution radio images.
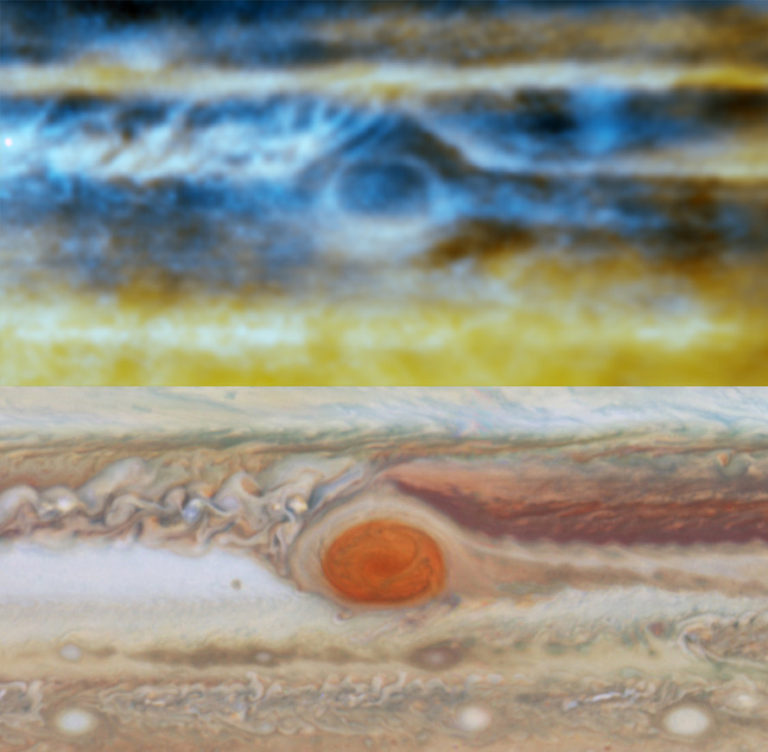
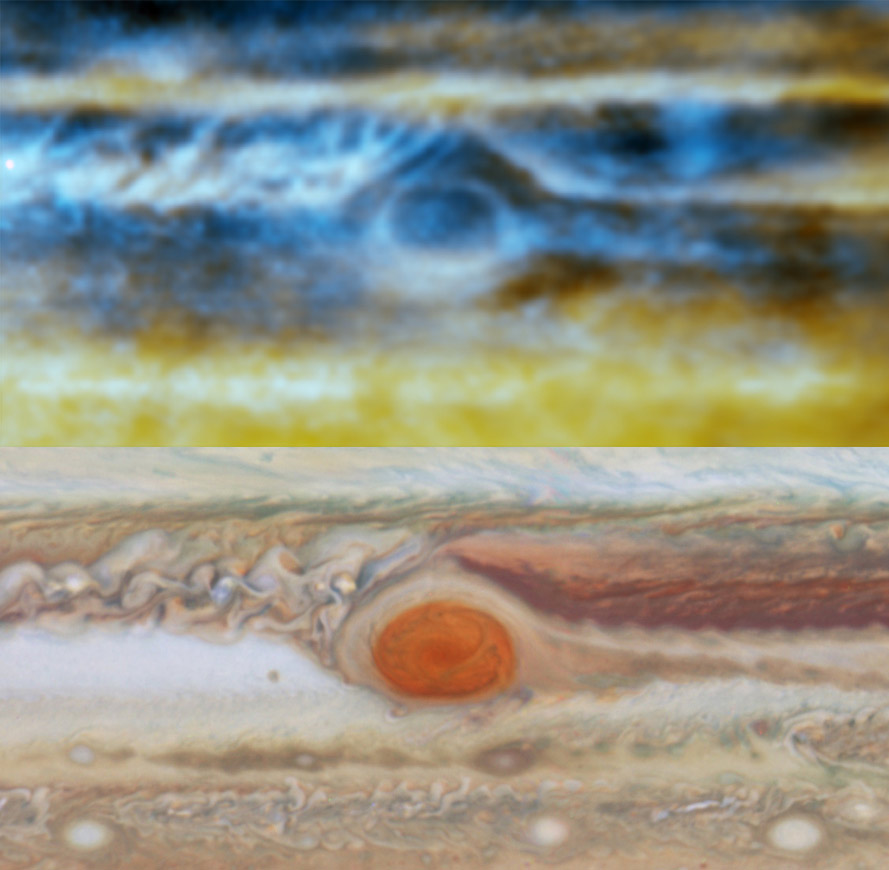
When the VLA was upgraded in 2011, it greatly increased its sensitivity and imaging capabilities. In 2013 the VLA gathered the first radio images of Jupiter’s atmosphere. It allowed us to peer into Jupiter’s thick atmosphere. Observations in visible light are limited by the cloud layer of Jupiter. But radio light penetrates these cloud layers more easily. The VLA observations let us see 100 kilometers below the visible clouds. They captured details of the great red spot, and how ammonia within Jupiter’s cloud layer rises and falls.
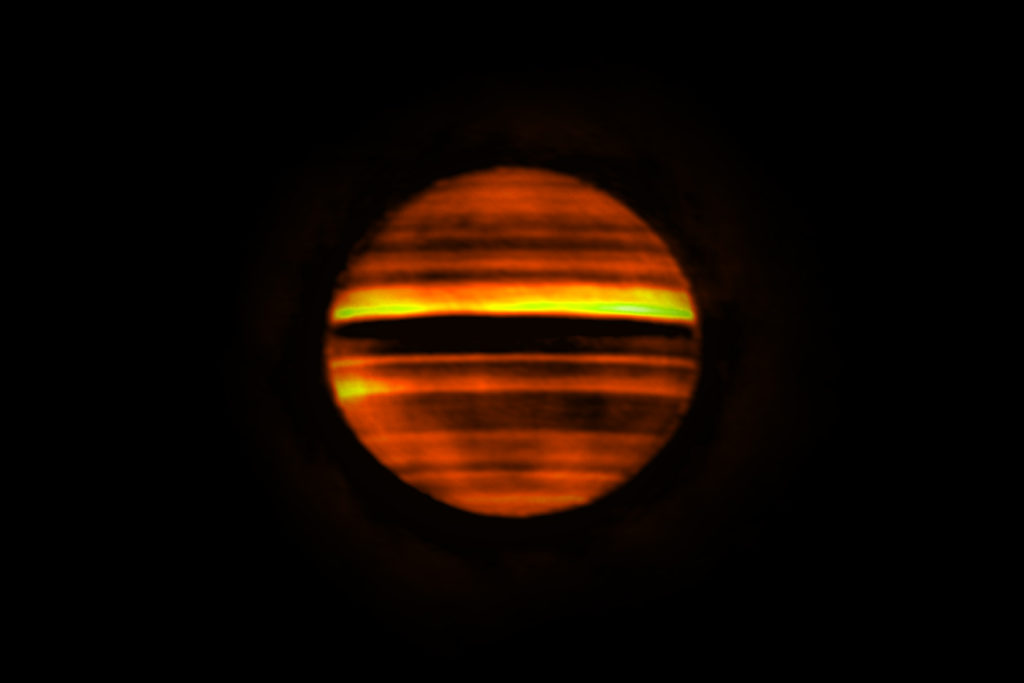
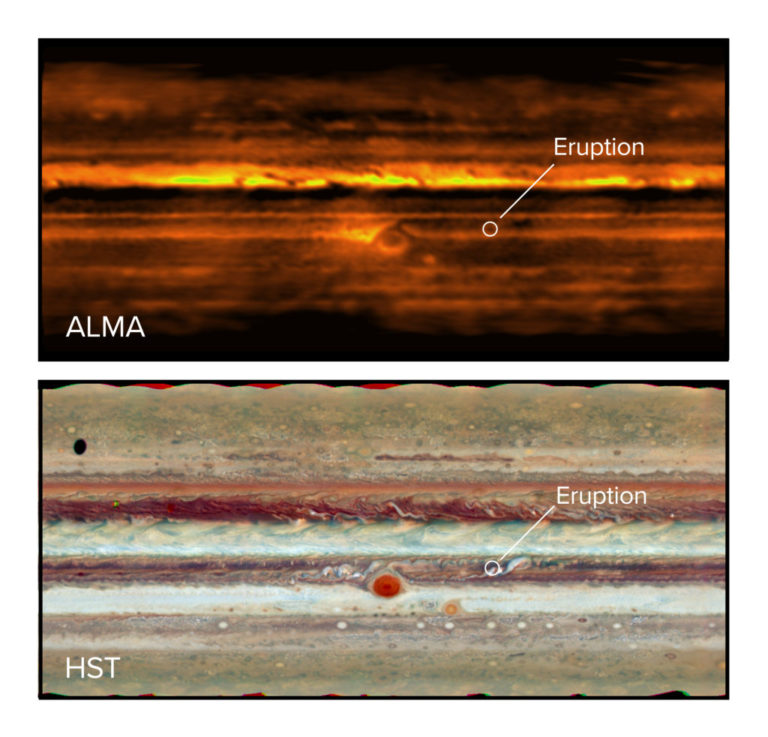
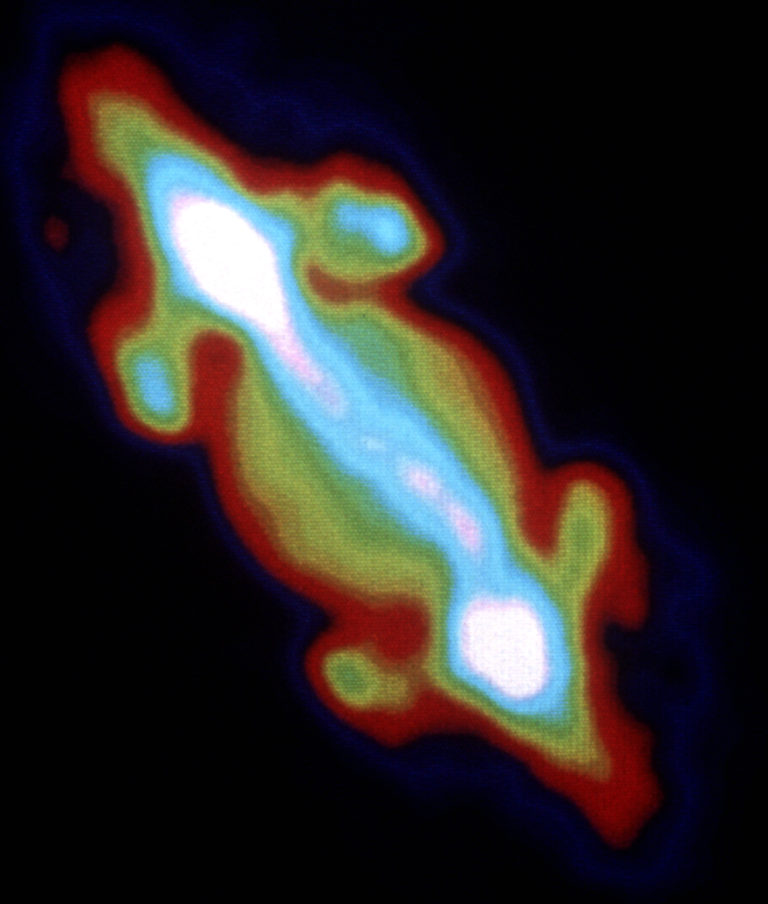
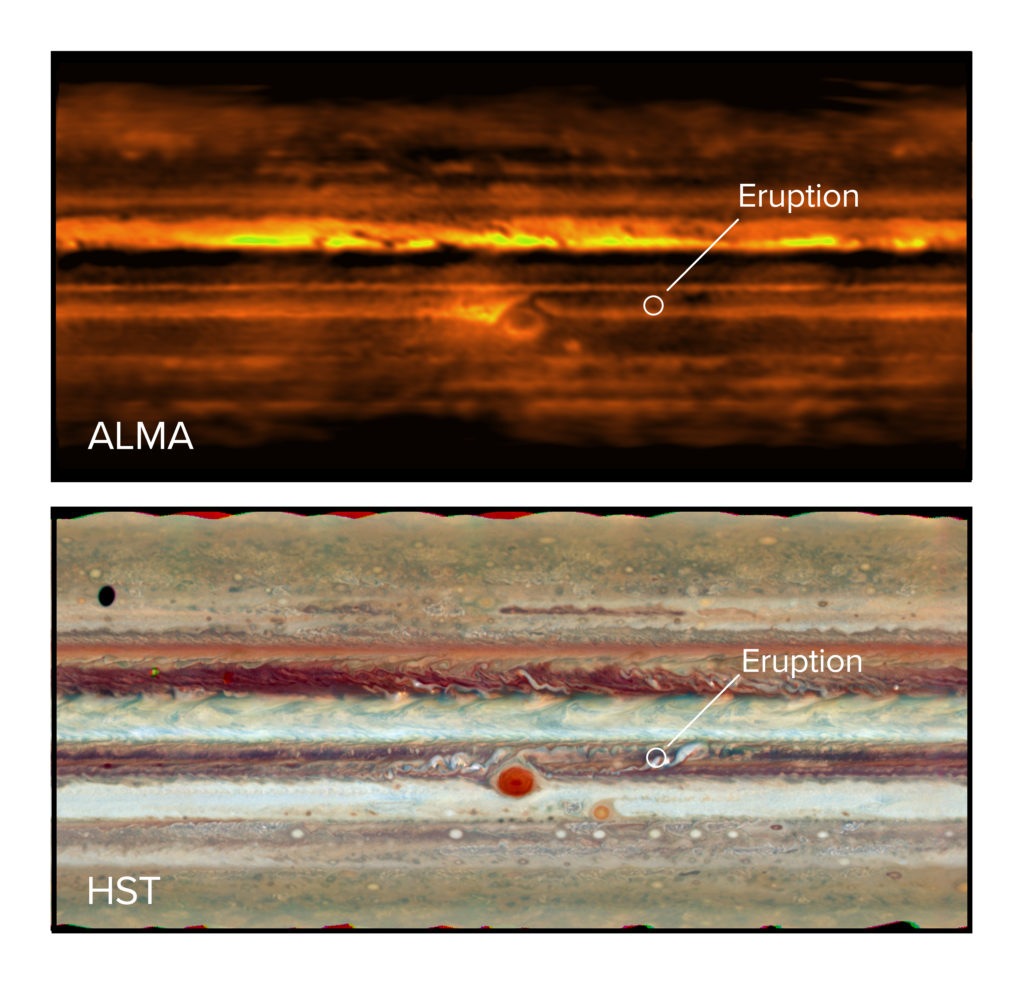
Recently the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) also captured even higher resolution images of Jupiter’s thermal emissions. ALMA operates at shorter wavelengths than the VLA. Since shorter wavelengths are absorbed more readily by Jupiter’s atmosphere, ALMA’s observation only penetrates about 50 kilometers below Jupiter’s cloud layer. But ALMA’s high resolution allowed astronomers to create a three-dimensional map of ammonia gas within the atmosphere. This helps us understand the mechanisms that drive storms on Jupiter.
As radio technology has advanced, the radio astronomy of Jupiter has become much more accessible. With only modest radio equipment, you can observe the radio light of Jupiter for yourselves. Projects such as NASA’s Radio JOVE encourage students and amateur scientists to observe radio emissions from Jupiter and other bright radio sources. The project teaches students about radio astronomy and engages in citizen science research projects.
Jupiter has long inspired humanity to look toward the stars. From Galileo’s first view through his telescope, to the radio arrays of the VLA and ALMA, the light of Jupiter at all wavelengths has much to offer.
Reference: de Pater, Imke, et al. “Peering through Jupiter’s clouds with radio spectral imaging.” Science 352.6290 (2016): 1198-1201.
Reference: de Pater, Imke, et al. “First ALMA Millimeter-wavelength Maps of Jupiter, with a Multiwavelength Study of Convection.” The Astronomical Journal 158.4 (2019): 139.