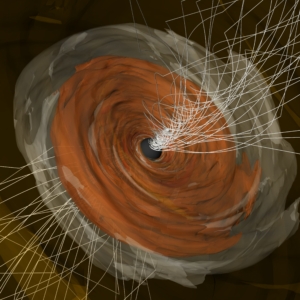
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) collaboration has published new results that describe for the first time how light from the edge of the supermassive black hole M87* spirals as it escapes the black hole’s intense gravity, a signature known as circular polarization.

Far, Far Away: Just How Distant Is That Galaxy?
Radio astronomers have observed galaxies billions of light years away. But how do they know just how far away those galaxies are?

Scientists Observe Gas Re-accretion in Dying Galaxies for the First Time
A new study from scientists using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) suggests that previously displaced gases can re-accrete onto galaxies, potentially slowing down the process of galaxy death caused by ram pressure stripping, and creating unique structures more resistant to its effects.
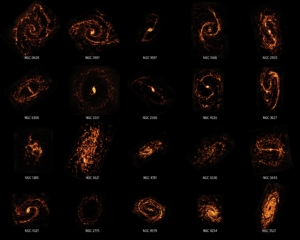
Cosmic Cartographers Map Nearby Universe Revealing the Diversity of Star-Forming Galaxies
A team of astronomers using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) has completed the first census of molecular clouds in the nearby Universe. The study produced the first images of nearby galaxies with the same sharpness and quality as optical imaging and revealed that stellar nurseries do not all look and act the same. In fact, they’re as diverse as the people, homes, neighborhoods, and regions that make up our own world.
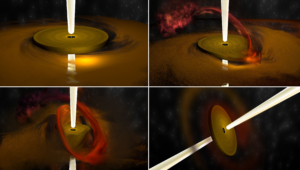
ALMA Shows Massive Young Stars Forming in “Chaotic Mess”
Astronomers used ALMA to study three young, high-mass stars and found, not the orderly, stable process of accreting new material seen in low-mass stars, but instead a “chaotic mess.” They conclude that their observations support a proposed “disordered infall” model for massive young stars that was supported by earlier computer simulations.

Record-breaking Stellar Flare From Nearby Star Recorded in Multiple Wavelengths for the First Time
Scientists using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) observed a record-breaking stellar flare from Proxima Centauri. The study also marks the first time that a powerful stellar flare, other than those from the Sun, has been observed with such complete wavelength coverage.





