The super-sharp radio “vision” of a continent-wide collection of NSF radio telescopes answered an outstanding question about the aftermath of the merger of two neutron stars.
First Science with ALMA’s Highest-Frequency Capabilities
Band 10, ALMA’s highest frequency vision, has given scientists a new view of jets of warm water vapor streaming away from a newly forming star and uncovered an astonishing assortment of molecules.
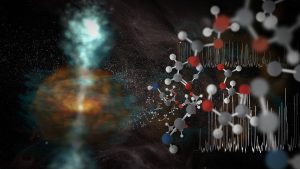
Pair of Colliding Stars Spill Radioactive Molecules into Space
Astronomers have made the first definitive detection of a radioactive molecule in interstellar space: a form, or isotopologue of aluminum monofluoride. The new data reveal that this radioactive isotopologue was created by the collision of two stars, a tremendously rare cosmic event that was witnessed on Earth as a “new star,” or nova, in the year 1670.
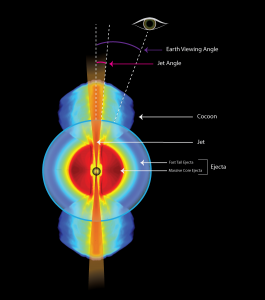
Enduring ‘Radio Rebound’ Powered by Jets from Gamma-Ray Burst
Astronomers using ALMA studied a cataclysmic stellar explosion known as a gamma-ray burst, or GRB, and found its enduring “afterglow.” The rebound, or reverse shock, triggered by the GRB’s powerful jets slamming into surrounding debris, lasted thousands of times longer than expected.
ALMA Finds Most-Distant Oxygen in the Universe
ALMA detects signature of oxygen from galaxy 13.28 billion light-years away
Image Release: ALMA Reveals Inner Web of Stellar Nursery
New data from ALMA and other telescopes reveal stunning web of filaments in the Orion Nebula.