The formation of massive stars and planets. The deaths of stars and galaxies. The extreme and violent behaviors of black hole jets and quasars. An up-close and personal radar view of the Moon. These mysteries and more were unraveled in 2021 by radio astronomers leveraging the scientific and technological power of National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) facilities.
The Baseline #10 – How To Kick A Pulsar Out Of The Galaxy
Pulsars are neutron stars. They are formed when an old star explodes as a supernova, so you would expect to find them in the center of its supernova remnant. But not always. Astronomers have learned that some pulsars are ejected from its remnant. The Very Large Array has discovered one pulsar that is quite a kick.
Join our host Summer Ash of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory as she talks about how you can get a kick out of pulsars.
VLA Reveals Double-Helix Structure in Massive Galaxy’s Jet
Astronomers used the VLA to trace a corkscrew-shaped magnetic field in a powerful jet of material ejected from the core of a massive galaxy farther away from the central galaxy’s central black hole than ever seen before. The new images provide clues that will help understand the mechanics of such jets, which are seen throughout the Universe.
ALMA Scientists Detect Signs of Water in a Galaxy Far, Far Away
Water has been detected in the most massive galaxy in the early Universe, according to new observations from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA). Scientists studying SPT0311-58 found H20, along with carbon monoxide in the galaxy, which is located nearly 12.88 billion light years from Earth. Detection of these two molecules in abundance suggests that the molecular Universe was going strong shortly after the elements were forged in early stars. The new research comprises the most detailed study of molecular gas content of a galaxy in the early Universe to date and the most distant detection of H20 in a regular star-forming galaxy.
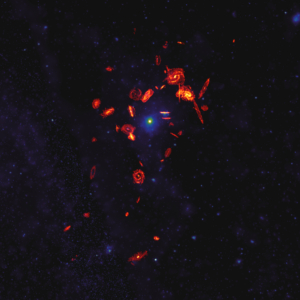
A Cosmic Whodunit: ALMA Study Confirms What’s Robbing Galaxies of Their Star-Forming Gas
Astronomers examining the nearby Universe with the help of the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) have just completed the largest high-resolution survey of star-forming fuel ever conducted in galaxy clusters. But more importantly, they’re tackling a long-standing mystery in astrophysics: what’s killing galaxies?
ALMA Scientists Uncover the Mystery of Early Massive Galaxies Running on Empty
Early massive galaxies—those that formed in the three billion years following the Big Bang—should have contained large amounts of cold hydrogen gas, the fuel required to make stars. But scientists observing the early Universe with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and the Hubble Space Telescope have spotted something strange: half a dozen early massive galaxies that ran out of fuel.