Multi wavelength composite astronomical image using data from the Jansky Very Large Array, Chandra X-ray Observatory, and optical data from the VLT and Subaru Telescopes.

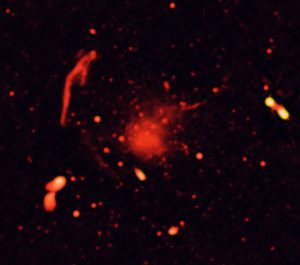
Abell 2744, Radio Only
Radio-only image of Abell 2744 region, showing radio-emitting features caused by subatomic particles accelerated to high speeds by the collisions of giant clusters of galaxies.
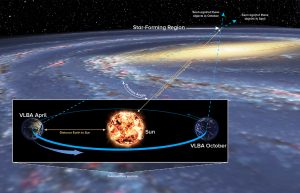
The Parallax Technique
The parallax technique determines distance by measuring the angle of apparent shift in an object’s position, as seen from opposite sides of Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Using this method, astronomers were able to directly measure the distance to a region on the far side of our Milky Way Galaxy, past the Galaxy’s center.
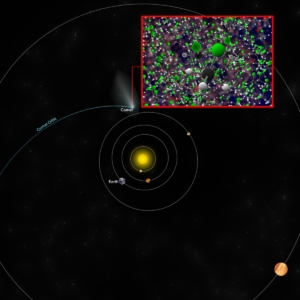
Methyl Chloride in Comet 67P/C-G
Approximate location of comet 67P/C-G when the Rosetta space probe discovered traces of methyl chloride — the same molecule detected by ALMA around the IRAS 16293-2422 star-forming region — along with other molecules.
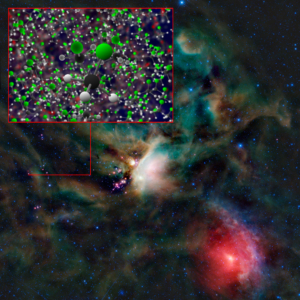
ALMA Finds Organohalogen Methyl Chloride Around Infant Stars
Organohalogen methyl chloride discovered by ALMA around the infant stars in IRAS 16293-2422. These same organic compounds were discovered in the thin atmosphere surrounding 67P/C-G by the Rosetta space probe. The background image of the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex is from NASA’s Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE).
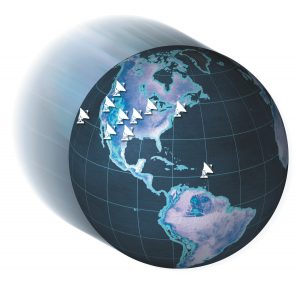
VLBA Global Locations
Artist’s conception of the Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA), a continent-wide radio telescope system. The VLBA is an interferometer consisting of 10 identical antennas on transcontinental baselines up to 8000 km (Mauna Kea, Hawaii to St. Croix, Virgin Islands). The VLBA is controlled remotely from the Science Operations Center in Socorro, New Mexico. Each VLBA station consists of a 25 m antenna and an adjacent control building. The received signals are amplified, digitized, and recorded on fast, high capacity recorders. The recorded data are sent from the individual VLBA stations to the correlator in Socorro.





