Latest NRAO News
News is managed by NRAO News & Public Information. Questions about News? Have a story to share? Want to interview a scientist or create new media about our telescopes?

Astronomers have unveiled the first image of the supermassive black hole at the center of our own Milky Way galaxy. This result provides overwhelming evidence that the object is indeed a black hole and yields valuable clues about the workings of such giants, which are thought to reside at the center of most galaxies. The image was produced by a global research team called the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) Collaboration, using observations from a worldwide network of radio telescopes.

Post-starburst galaxies were previously thought to scatter all of their gas and dust—the fuel required for creating new stars—in violent bursts of energy, and with extraordinary speed. Now, new data from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) reveals that these galaxies don’t scatter all of their star-forming fuel after all. Instead, after their supposed end, these dormant galaxies hold onto and compress large amounts of highly-concentrated, turbulent gas. But contrary to expectation, they’re not using it to form stars.

Scientists studying V Hydrae (V Hya) have witnessed the star’s mysterious death throes in unprecedented detail. Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and data from the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), the team discovered six slowly-expanding rings and two hourglass-shaped structures caused by the high-speed ejection of matter out into space.
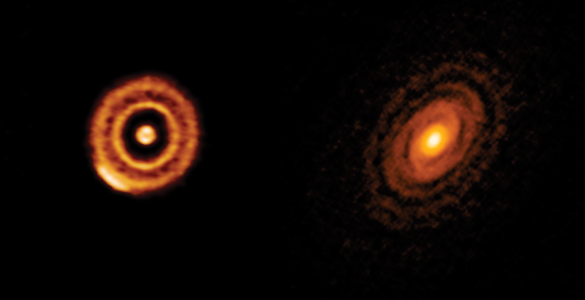
Astronomers have discovered more than 5,000 planets orbiting other stars. We now know that most stars have orbiting planets…

The formation of massive stars and planets. The deaths of stars and galaxies. The extreme and violent behaviors of black hole jets and quasars. An up-close and personal radar view of the Moon. These mysteries and more were unraveled in 2021 by radio astronomers leveraging the scientific and technological power of National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) facilities.

Scientists using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) made a rare detection of a likely stellar flyby event in the Z Canis Majoris (Z CMa) star system. An intruder—not bound to the system—object came in close proximity to and interacted with the environment surrounding the binary protostar, causing the formation of chaotic, stretched-out streams of dust and gas in the disk surrounding it.

The National Science Foundation (NSF) and the board of the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) have approved a multi-million dollar upgrade project for the Observatory’s 1.3mm (Band 6) receivers through the North American ALMA Development Program. The receivers—originally built, and to be upgraded, by the Central Development Laboratory (CDL) at the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO)—are the most scientifically productive in ALMA’s lineup.

Water has been detected in the most massive galaxy in the early Universe, according to new observations from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA). Scientists studying SPT0311-58 found H20, along with carbon monoxide in the galaxy, which is located nearly 12.88 billion light years from Earth. Detection of these two molecules in abundance suggests that the molecular Universe was going strong shortly after the elements were forged in early stars. The new research comprises the most detailed study of molecular gas content of a galaxy in the early Universe to date and the most distant detection of H20 in a regular star-forming galaxy.
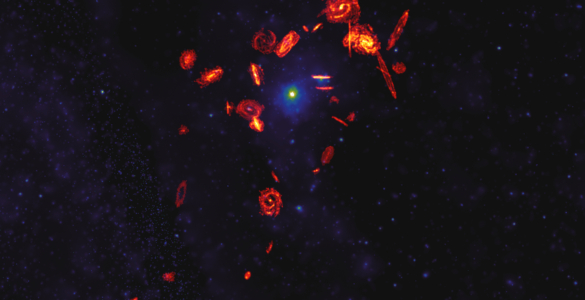
Astronomers examining the nearby Universe with the help of the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) have just completed the largest high-resolution survey of star-forming fuel ever conducted in galaxy clusters. But more importantly, they’re tackling a long-standing mystery in astrophysics: what’s killing galaxies?

Early massive galaxies—those that formed in the three billion years following the Big Bang—should have contained large amounts of cold hydrogen gas, the fuel required to make stars. But scientists observing the early Universe with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and the Hubble Space Telescope have spotted something strange: half a dozen early massive galaxies that ran out of fuel.





