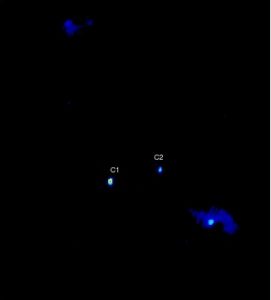
VLBA image of the central region of the galaxy 0402+379, showing the two cores, labeled C1 and C2, identified as a pair of supermassive black holes in orbit around each other.
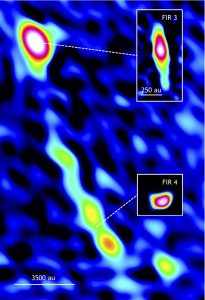
Star’s Birth May Have Triggered Another Star Birth
Protostar FIR 3 (HOPS 370) with outflow that may have triggered the formation of younger protostar FIR 4 (HOPS 108), in the Orion star-forming region. Pullouts are individual VLA images of each protostar. (au = astronomical unit, the distance from the Earth to the Sun, about 93 million miles.)

Chaotically Magnetized Cloud Is No Place to Build a Star, or Is It?
For decades, scientists thought that the magnetic field lines coursing around newly forming stars were both powerful and unyielding, working like jail bars to corral star-forming material. More recently, astronomers have found tantalizing evidence that large-scale turbulence far from a nascent star can drag magnetic fields around at will. Now, a team of astronomers using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) has discovered a surprisingly weak and wildly disorganized magnetic field very near a newly emerging protostar, shown here in an artist’s impression. These observations suggest that the impact of magnetic fields on star formation is more complex than previously thought.
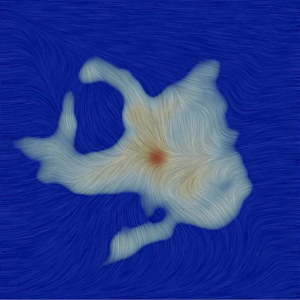
The Magnetic Field of Ser-emb 8
Texture represents the magnetic field orientation in the region surrounding the Ser-emb 8 protostar, as measured by ALMA. The gray region is the millimeter wavelength dust emission.

VLA Gives New Insight Into Galaxy Cluster’s Spectacular “Mini-Halo”
Astronomers using the National Science Foundation’s Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) have discovered new details that are helping them decipher the mystery of how giant radio-emitting structures are formed at the center of a cluster of galaxies. The scientists studied a cluster of thousands of galaxies more than 250 million light-years from Earth, named the Perseus Cluster after the constellation in which it appears. Embedded within the center, the Perseus Cluster hosts a pool of superfast particles that emit radio waves, creating a radio structure known as a “mini-halo.” Mini-haloes have been found in about 30 galaxy clusters, but the halo in the Perseus Cluster is the largest known, about 1.3 million light-years in diameter, or 10 times the size of our Milky Way Galaxy. Radio emission in red; optical in white.
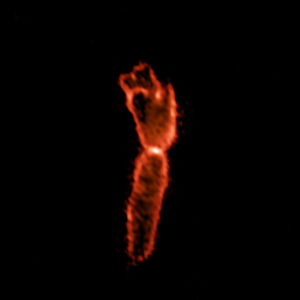
The Ultra-Cold Outflow of the Boomerang Nebula
The Boomerang Nebula, a pre-planetary nebula produced by a dying star. ALMA observations show the hourglass-shaped outflow, which is embedded inside a roughly round ultra-cold outflow. The hourglass outflow stretches more than three trillion kilometers from end to end (about 21,000 times the distance from the Sun to the Earth), and is the result of a jet that is being fired by the central star, sweeping up the inner regions of the ultra-cold outflow like a snow-plow. The ultra-cold outflow is about 10 times bigger.





