Latest NRAO News
News is managed by NRAO News & Public Information. Questions about News? Have a story to share? Want to interview a scientist or create new media about our telescopes?

ALMA has detected a star in a binary system that may have formed like a planet.
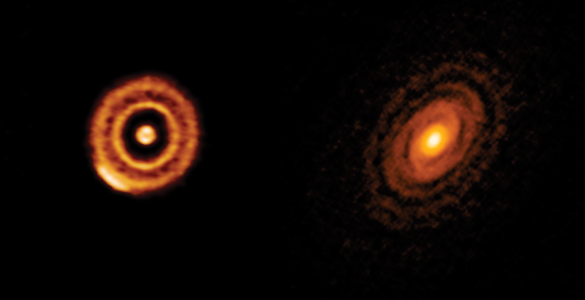
ALMA has conducted a survey of protoplanetary disks, the planet-forming dust belts around young stars.

New ALMA data reveal distinct streamers of material being pulled from three smaller galaxies into the larger galaxy W2246-0526, the most luminous known galaxy in the universe.

A billion light-years from Earth lies one of the universe’s most massive structures, a giant surrounded by a sprawling…
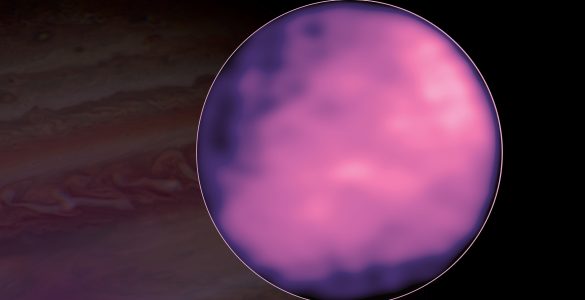
New ALMA images show never-before-seen surface details on Europa, including an enigmatic “cold spot.”

Using ALMA, an international team of astronomers found evidence that a white dwarf and a brown dwarf collided in a short-lived blaze of glory.
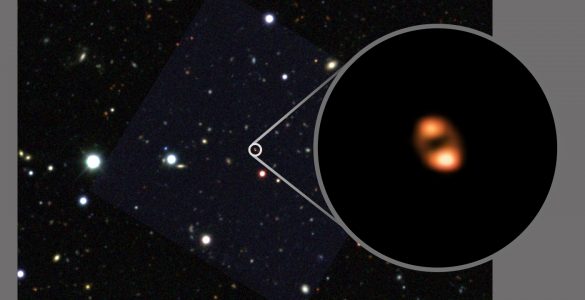
Astronomers using ALMA, with the aid of a gravitational lens, have detected the most-distant galactic “wind” of molecules ever observed, seen when the universe was only one billion years old. By tracing the outflow of hydroxyl (OH) molecules – which herald the presence of star-forming gas in galaxies – the researchers show how some galaxies in the early universe quenched an ongoing wildfire of starbirth.
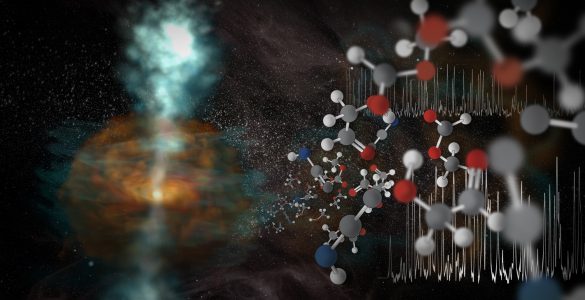
Band 10, ALMA’s highest frequency vision, has given scientists a new view of jets of warm water vapor streaming away from a newly forming star and uncovered an astonishing assortment of molecules.

Astronomers have made the first definitive detection of a radioactive molecule in interstellar space: a form, or isotopologue of aluminum monofluoride. The new data reveal that this radioactive isotopologue was created by the collision of two stars, a tremendously rare cosmic event that was witnessed on Earth as a “new star,” or nova, in the year 1670.
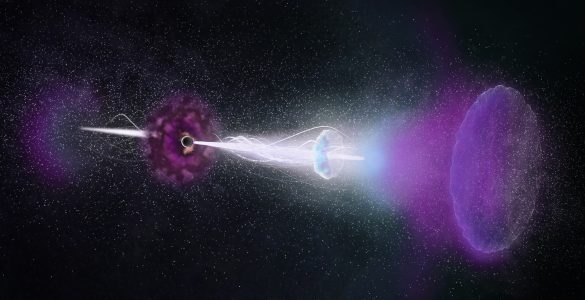
Astronomers using ALMA studied a cataclysmic stellar explosion known as a gamma-ray burst, or GRB, and found its enduring “afterglow.” The rebound, or reverse shock, triggered by the GRB’s powerful jets slamming into surrounding debris, lasted thousands of times longer than expected.





