Glossary of Radio Astronomy Terms
Kelvins (Kelvin):
A scale that measures an object’s temperature over absolute zero, which is the lower limit of thermodynamic temperature. A particle at this temperature would experience almost no motion whatsoever, only experiencing motion due to quantum effects.
Kiloparsec:
A unit of measurement that looks at the distance between earth and objects outside of our solar system. One kiloparsec equals a distance of 1000 parsecs (3260 light-years about 19.56 quadrillion miles).
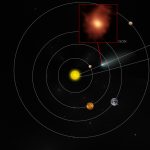
Kuiper belt:
A region of our solar system beyond the orbit of Neptune. It contains many comets, asteroids, and other icy bodies. Pluto is often considered a large resident of this region. Other star systems likely sport similar regions.

Keplerian rotation:
The orderly motion of objects around a central mass, like planets and asteroids in our solar system. The speed — or orbital periods — of these objects is determined by their distance from the central mass (or Sun in the case of our solar system). The closer in the object the faster it orbits.